First, explain why the money demand curve is downward sloping. Second, explain what factor(s) will cause shifts in the money demand curve
What will be an ideal response?
The money demand curve is downward sloping (with the interest rate on the vertical axis). It is assumed that money pays no interest. At the same time, individuals earn interest when they hold bonds. So, as the interest rate increases, individuals are more willing to incur the costs associated with converting bonds to money when they wish to buy goods. So, an increase in the interest rate causes a reduction in money demand. Money demand depends on the level of transactions and on the interest rate. As the level of transactions increases, individuals will increase money demand. Assuming that nominal income is correlated with nominal transactions, an increase in nominal income will cause an increase in money demand and shifts in the curve.
You might also like to view...
Gomer can make either 200 gallons of corn liquor (L) or 200 gallons of strawberry wine (W) every six months. Goober can make only 100 gallons of corn liquor (L) or 50 gallons of strawberry wine (W) every six months. Which statement below is true?
A) Gomer produces W more efficiently than Goober. B) Gomer produces L less efficiently than Goober. C) Goober produces L more efficiently than Gomer. D) All of the above are true.
Suppose biochemists discover an enzyme that can double the amount of ethanol that may be derived from a given amount of biomass. Based on this technological development, we expect the:
A) supply curve for ethanol to shift leftward. B) supply curve for ethanol to shift rightward. C) demand curve for ethanol to shift leftward. D) demand curve for ethanol to shift rightward.
Refer to the table below. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 75 percent chance of being $5 and a 25 percent chance of being $9. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
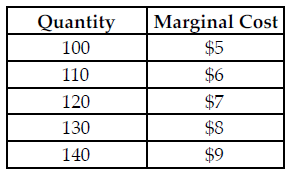
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
A) 130 B) 110 C) 100 D) 120
Declining cost industries
a. have upward rising AC curves. b. have upward rising demand curves. c. have ?-shaped total costs. d. have diseconomies of scale. e. have marginal cost curves below their average cost curve.