Determine the heat transfer area requirements of Problem 10.40 if (a) 1-2 shell and tube, (b) an unmixed crossflow, and (c) a parallel flow heat exchanger are used, respectively.
GIVEN
• An air-to-gas heat exchanger
• Entering temperatures
? Ta,in = 350°C
? Tg,in = 700°C
• Mass flow rates: ma = mg = 5 kg/s
• Specific heats: cpa = cpg = 1.05 kJ/(kg K) = 1050 J/(kg K)
• Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) = 75 W/(m2 K)
FIND
The heat transfer area (A) as a function of the effectiveness (e) for (a) A 1-2 shell and tube heat exchanger (b) An unmixed crossflow heat exchanger (c) A parallel flow heat exchanger
ASSUMPTIONS
• For case (a) the air is in the tubes
SKETCH
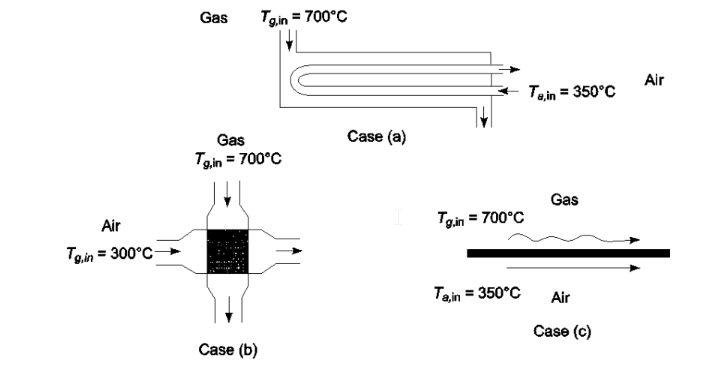
for counterflow
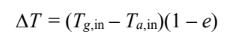
This must be corrected for case (a) and (b) where
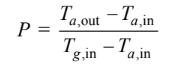
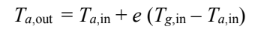
Therefore P = e
Since
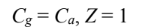
The solution for parts (a) and (b) are the same expect that the mean temperature (?T) must be multiplied by the factor F with the following results
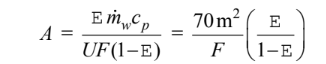
where F for part (a) and for part (b) where P = e and Z = 1.0.
(c) For parallel flow
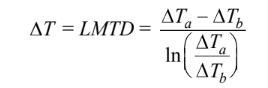
Where:
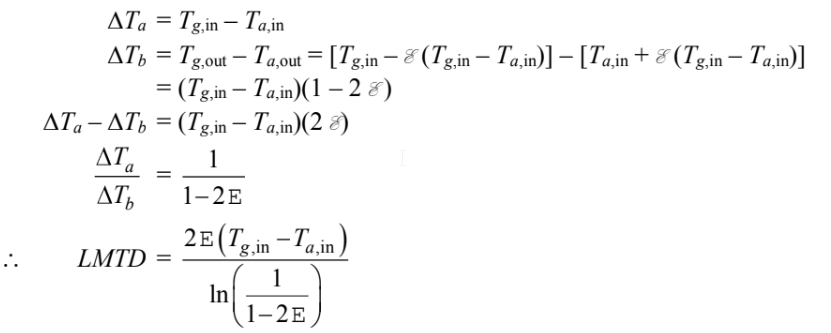
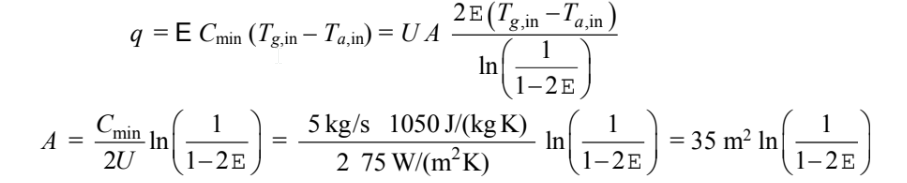
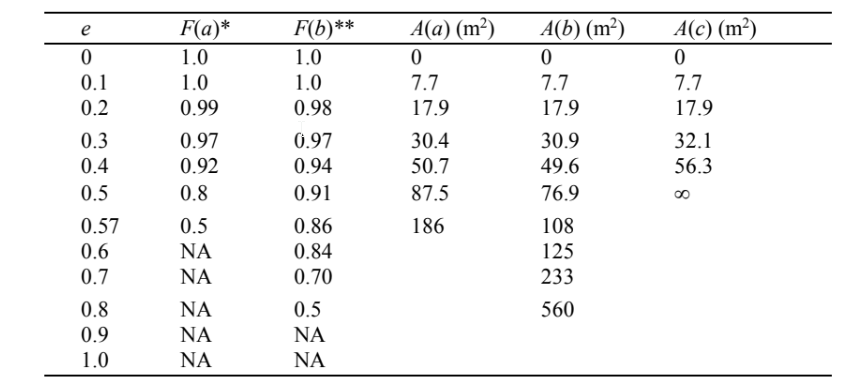
Tabulating these results
You might also like to view...
Which of the following best summarizes what we mean by dark matter?
A) matter that we have identified from its gravitational effects but that we cannot see in any wavelength of light B) matter that may inhabit dark areas of the cosmos where we see nothing at all C) matter consisting of black holes D) matter for which we have theoretical reason to think it exists, but no observational evidence for its existence
Bumpers on cars are not of much use in a collision. To see why, calculate the average force a bumper would have to exert if it brought a 1200-kg car (a so-called compact model) to a rest in 15 cm
when the car had an initial speed of 2.0 m/s (about 4.5 mph). (Bumpers are built with springs that compress to provide a stopping force without, hopefully, denting the metal.) A) 3.2 × 104 N B) 1.6 × 104 N C) 5.4 × 104 N D) 1.8 × 104 N E) 6.5 × 105 N
The "seeing" ability or resolution of radiation is determined by its wavelength. If the size of an atom is approximately 1.3 × 10^?10 m, how fast must an electron travel to have a wavelength smaller than that of an atom? (me = 9.11 × 10^?31 kg and h = 6.63 × 10^?34 J?s)
a. 5.6E+6 m/s b. 5.1E+7 m/s c. 8.4E+5 m/s d. 9.5E+6 m/s e. 2.4E+3 m/s
Refracting Telescope: The objective lens of a telescope has a focal length of 2.0 m and its eyepiece has a focal length of 1.0 cm. What is the magnification of this telescope when viewing Jupiter?
A. 0.0050 B. 0.50 C. 2.0 D. 20 E. 200