What determines the ability of these factors to shift the short-run aggregate supply curve, to shift the long-run aggregate supply curve, or to shift both curves?
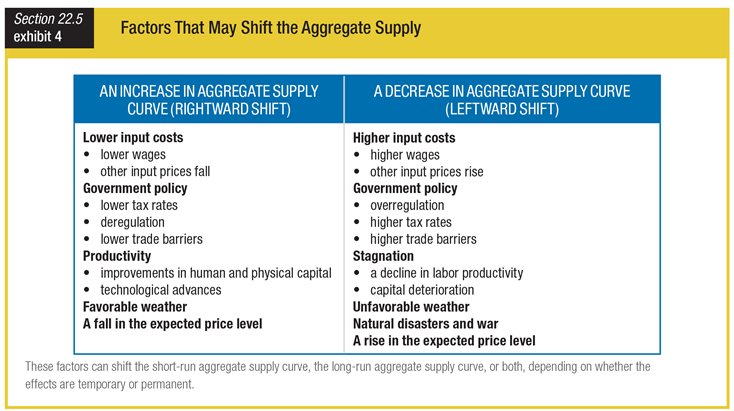
a. whether or not the effects cause changes in the overall price level
b. whether the effects are temporary or permanent
c. whether or not producers are fooled by the misperception effect
d. whether the effects are positive or negative
b. whether the effects are temporary or permanent
You might also like to view...
When output is below its full-employment level, the short-run aggregate supply will shift down and to the right because
A) the expected price level will be below the actual price level. B) workers' wages will decline. C) prices of nonlabor inputs will rise. D) workers' wages will rise.
If we add together all the gains from specialization and trade and then subtract all the losses, the net result would be
A. Positive: a net gain for the world and each country. B. Negative: a net loss for the world and each country. C. Impossible to tell: the net result could be zero, positive, or negative. D. Zero: the gains and losses would cancel out.
When the IMF provides loans to developing countries, it often requires these countries to adopt:
A. a contractionary fiscal policy and an expansionary monetary policy. B. contractionary monetary and fiscal policies. C. expansionary monetary and fiscal policies. D. a contractionary monetary policy and an expansionary fiscal policy.
Because a monopoly ignores external costs, it is possible that it will
A) produce the socially optimal quantity of a good. B) produce more than the socially optimal quantity of a good. C) produce less than the socially optimal quantity of a good. D) All of the above.