A small 4.0-µC charge and a small 1.5-µC charge are initially very far apart
How much work does it take to bring them to a final configuration in which the 4.0-µC charge is at the point x = 1.0 mm, y = 1.0 mm, and the 1.5-µC charge is at the point x = 1.0 mm, y = 3.0 mm? (k = 1/4??0 = 8.99 × 109 N ? m2/C2 )
A) 27 J
B) 13.5 kJ
C) 54 J
D) 13.5 J
A
You might also like to view...
Suppose a uniform electric field of 4 N/C is in the positive x direction. When a charge is placed at and fixed to the origin, the resulting electric field on the x axis at x = 2 m becomes zero. What is the magnitude of the electric field at x = 4 m on the x axis at this time?
a. 0 b. 1 N/C c. 2 N/C d. 4 N/C e. More information is needed to find the resulting field magnitude at this position.
Which of the following types of protogalactic clouds is most likely to form an elliptical galaxy?
A) a low-density cloud with quite a bit of angular momentum B) a dense cloud with quite a bit of angular momentum C) a very low-density cloud with very little angular momentum D) a very massive cloud with any density and a lot of angular momentum E) a dense cloud with very little angular momentum
Lenz's Law: An outer metal ring surrounds an inner metal ring, as shown in the figure. The current in the outer ring is counterclockwise and decreasing. What is the direction of the induced current in the inner ring?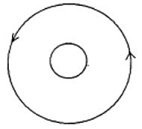
A. clockwise B. counterclockwise C. There is no induced current in the inner ring.
A rectangular coil of 100 turns measures 40.0 cm by 20.0 cm. This coil is placed next to an electromagnet which is switched on, increasing the magnetic field through the coil from zero to 0.800 T in 50.0 ms. If the resistance of the coil is 2.0 ohms, what are the induced voltage and current in the coil?