A stainless steel pin fin 5-cm-long, 6-mm-OD, extends from a flat plate into a 175 m/s air stream as shown in the sketch. Estimate (a) the average heat transfer coefficient between air and the fin. (b) the temperature at the end of the fin. (c) the rate of heat flow from the fin with glycerol at 20°C flowing over the fin at 2 m/s. The plate temperature is 50°C.
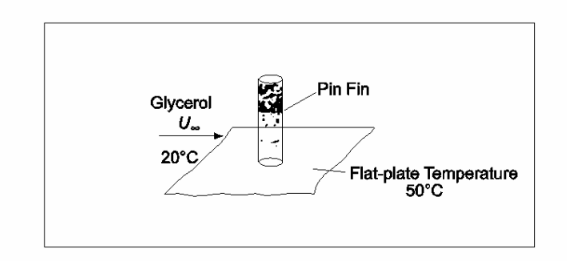
GIVEN
• A stainless steel pin fin in an air stream
• Pin length (L) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
• Pin diameter (D) = 6 mm = 0.006 m
• Glycerol velocity (U?) = 2 m/s
• Glycerol temperature (T?) = 20°C
• Plate temperature (Tp) = 50°C FIND
(a) The average heat transfer coefficient ( h c) (b) The temperature of the end of the fin (TL) (c) The rate of heat flow from the fin (qf) ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Turbulence in the glycerol approaching the fin is low
• Radiative heat transfer is negligible
• Steel is type 304
• Steel properties are uniform
• Variation of the thermal properties of glycerol and steel with temperature is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.285 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 1175 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 12,609 for type 304 stainless steel ks = 14.4 W/(m K) at 20°C
(a) The Reynolds number is
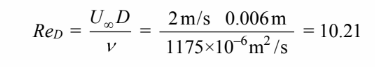
Therefore, Equation may be used. (Note that Pr/Prs = 1)
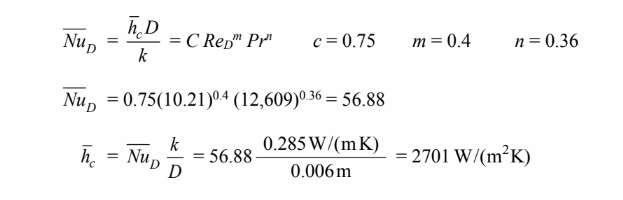
(b)
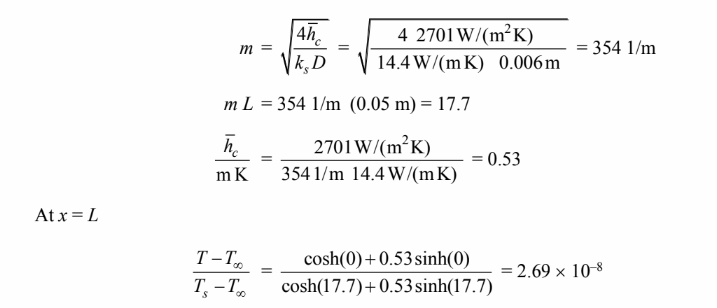
Therefore, the tip temperature is practically the same as the ambient glycerol temperature.
(c) The rate of heat transfer,

You might also like to view...
Ohm's Law: The figure shows electrons passing through a resistor. The arrow shows the direction in which the electrons are moving. Which of the following statements are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)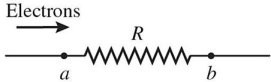
A. The electrons are moving slower at point b than at point a. B. The electric potential is higher at point b than at point a. C. The electric potential is lower at point b than at point a. D. The electrons are losing electric potential energy as they move through the resistor from a to b. E. The speed of the electrons at point b is the same as it is at point a.
One way to probe the rate of nuclear reactions in the center of the Sun is by studying ________ produced because ________.
A. neutrinos; they pass out of the Sun without undergoing a random walk B. positrons; they annihilate into gamma rays of very specific energies C. wave motions; they can be measured at the Sun's surface D. heavy hydrogen; it has different spectral lines than normal hydrogen
Process of Science: Why do we think the source of Jupiter's large internal energy come from gravitational contraction?
What will be an ideal response?
A helium nucleus?
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. zero F. Other G. AA H. BB I. CC J. DD