Quantitative easing is a central bank policy that attempts to stimulate the economy by possibly
A) selling treasury securities.
B) making discount loans to nonfinancial corporations.
C) slowly reducing the required reserve ratio.
D) buying long-term securities.
D
You might also like to view...
When the overall price level in an economy increases, the interest rate in that economy tends to increase as well. This increase in the interest rate makes investing in domestic assets look more attractive than investing in assets in other countries, so the demand for foreign assets decreases. This is called the _____
a. interest rate effect b. exchange rate effect c. wealth effect d. accelerator effect
A tax accounting firm produces 500 tax returns units when the market price is $150 per return and produces 700 tax returns when the market price is $170 per tax return. Using the midpoint method, for this range of prices, the price elasticity of supply is about
a. 2.67. b. 0.67. c. 0.4. d. 0.125.
If wage rates fall at the same time that labor productivity increases, what is the effect on short-run aggregate supply (SRAS)?
A) SRAS falls. B) SRAS remains constant. C) SRAS rises. D) SRAS may rise, fall, or remain constant.
Joe is the owner of the 7-11 Mini Mart, Sam is the owner of the SuperAmerica Mini Mart, and together they are the only two gas stations in town. Currently, they both charge $3 per gallon, and each earns a profit of $1,000. If Joe cuts his price to $2.90 and Sam continues to charge $3, then Joe's profit will be $1,350, and Sam's profit will be $500. Similarly, if Sam cuts his price to $2.90 and Joe continues to charge $3, then Sam's profit will be $1,350, and Joe's profit will be $500. If Sam and Joe both cut their price to $2.90, then they will each earn a profit of $900. You may find it easier to answer the following questions if you fill in the payoff matrix below. 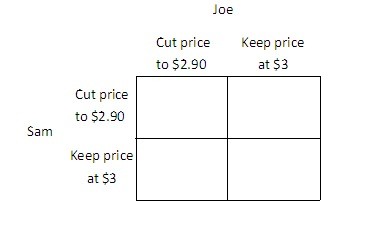
width="383" />For both Joe and Sam, ________ is a ________. A. leaving the price at $3; dominant strategy B. cutting the price to $2.90; dominated strategy C. leaving the price at $3; Nash equilibrium D. cutting the price to $2.90; dominant strategy