In short run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry whose firms are earning economic profits, a firm:
a. has no incentive to change its output
b. has no incentive to change its plant size.
c. has no incentive to expand its factory.
d. has no incentive to leave the industry.
a
You might also like to view...
Refer to Resource Supply/Demand. What does area D represent?
The following questions refer to the accompanying graph, which shows the supply and demand for a resource. The owner of the resource is receiving the price P0 and is providing the quantity Q0.
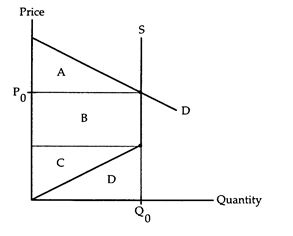
a. The value that Q0 units of the resource gives to demanders.
b. The revenue generated from selling Q0 units of the resource.
c. The rent that resource owner earns from providing Q0 units.
d. The minimum payment needed for the resource owner to supply Q0 units.
Diminishing marginal utility of wealth leads to risk aversion because at a given level of wealth a dollar gained
A) is worth more in additional utility than a dollar lost. B) is worth less in additional utility than a dollar lost. C) is worth as much in additional utility as a dollar lost. D) does not add to total utility.
The bond markets are important because they are
A) easily the most widely followed financial markets in the United States. B) the markets where foreign exchange rates are determined. C) the markets where interest rates are determined. D) the markets where all borrowers get their funds.
Because a monopolist must cut its price to increase its sales by one unit,
A. MR > P at every output level. B. MC > MR at every output level. C. P > MR at every output level. D. MC > P at every output level.