If government spending and the price level increase, then
A) the interest rate decreases, consumption increases, and investment spending increases.
B) the interest rate decreases, consumption declines, and investment spending declines.
C) the interest rate increases, consumption declines, and investment spending declines.
D) the interest rate increases, consumption increases, and investment spending increases.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Budget Lines. Which of the following changes is consistent with the situation shown in the diagram?
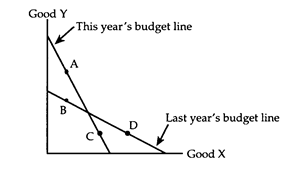
a. The consumer's income fell.
b. The relative price of good X in terms of good Y fell.
c. The absolute price of good X rose, and the absolute price of good Y fell.
d. The absolute price of both goods rose, with the price of good X rising by the higher percentage.
Real GDP in the country of Oz is growing at 5 percent and its population is growing at 2 percent. In the country of Lilliput, real GDP is growing at 4 percent and its population is growing at 0.5 percent. Thus,
A) real GDP per person in Oz is growing at a faster rate than in Lilliput. B) real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing at a faster rate than in Oz. C) real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing at the same rate as in Oz. D) real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing at a rate that is not comparable to that in Oz. E) We need more information to determine if real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing faster or slower than real GDP per person in Oz.
Trading partners should specialize in producing goods in accordance with comparative advantage, then trade and diversify in consumption because
a. out-of-pocket costs of production decline b. free trade areas protect infant industries c. economies of scale are present d. manufacturers face diminishing returns e. more goods are available for consumption
Which of the following types of unemployment is the hardest to reduce?
a. Cyclical unemployment b. Structural unemployment c. Voluntary unemployment d. Frictional unemployment e. Seasonal unemployment