The plate gradually oxidizes over time so that the surface emissivity increases to 0.5. Calculate the resulting temperature in the plate including radiation heat transfer to the surroundings at the same temperature as the ambient temperature.
GIVEN
Plate in Problem 4.34 oxidizes
FIND
(a) New temperature distribution considering radiation heat transfer
ASSUMPTIONS
(a) Neglect temperature gradients through the plate thickness
SKETCH
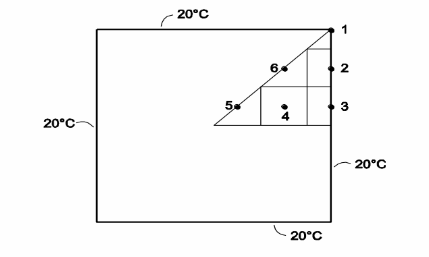
Addition of radiative heat transfer from the plate can be most easily handled by computing the radiative heat transfer coefficient for each node (using the temperature for the node calculated from the previous iteration) and by then adding this radiative heat transfer coefficient to the convective heat transfer coefficient for the present iteration. The radiative heat transfer coefficient for node i is
hri= ? ? (Ti2 + T?2) (Ti + T?). The following table gives the results for the Gauss-Seidel iteration. (Recall that temperature must be expressed in Kelvins.)
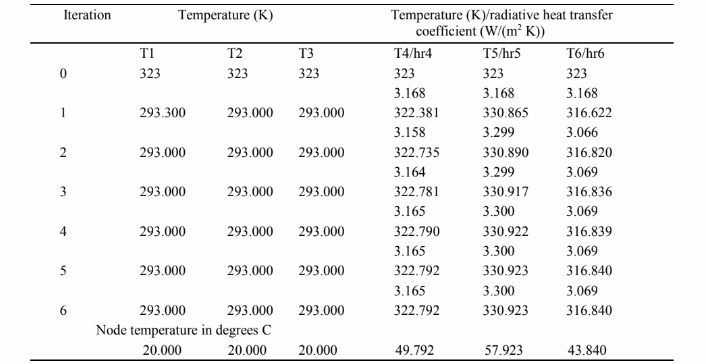
The peak temperature has been reduced by about 9.8 K due to radiation.
You might also like to view...
The globular star clusters are the most obvious examples of Population II around us
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The average distance from Earth to the sun is defined as one astronomical unit (AU). If an asteroid orbits the sun in 1/3 of a year in a circular orbit, the asteroid's distance from the sun is closest to
A) 0.48 AU. B) 0.19 AU. C) 2.1 AU. D) 0.33 AU. E) 5.2 AU.
Draw the structural formula for methyl alcohol
The deviation of a lens from its ideal behavior is referred to as
A) spherical aberration. B) chromatic aberration. C) an aberration. D) achromatic aberration. E) None of the other choices is correct.