Price fixing is collusive and illegal under U.S. antitrust laws. Predatory pricing, price discrimination, and tying have less obvious effects and are sometimes practiced by non- colluding oligopolists. Describe at least two of these strategies and explain the circumstances under which they raise regulatory concern.
What will be an ideal response?
Predatory pricing entails setting a price deliberately low in order to drive out
competitors. Proving that a firm lowered its prices for that motive is difficult. Regulators
would be most concerned if a firm cut its prices, a competitor was forced out of the
market, and then the original firm raised its prices to the monopoly level. Price
discrimination involves charging different prices to different groups of consumers. It can
be challenged under the Robinson-Patman Act. It would raise antitrust concerns only if
it was used as part of a strategy to block entry to a market or force a competitor out of
the market. Tie-in-sales require a buyer to purchase a product (a tied good) that is
needed to use another product (the tying good) sold by the same firm. Tying is
problematic from a legal standpoint when it is perceived as excessively expanding the
seller’s market power.
You might also like to view...
Economists conclude that the only way to measure fairness is
A) to insure that the rules are fair. B) to insure that the result is fair. C) to insure that both the rules and the result are fair. D) to compare the allocatively efficient quantity to the equilibrium quantity. E) None of the above answers is correct.
After a particular loan has been paid off, neither the borrower nor the lender has lost purchasing power. Therefore, it must be true that actual inflation was
a. greater than expected inflation. b. equal to expected inflation. c. less than expected inflation. d. greater than the nominal rate of interest.
Which of the following is not a possible source of last-minute reserves for a private bank?
A. Selling bonds. B. Borrowing reserves from other banks. C. Raising the discount rate. D. Borrowing reserves from the Federal Reserve System.
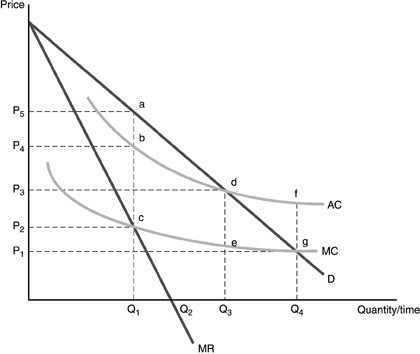 Refer to the above figure. From the standpoint of society, the optimal output is
Refer to the above figure. From the standpoint of society, the optimal output is
A. Q1 B. Q2 C. Q3 D. Q4