A 3.0-kg mass is dropped from the edge of a 50-m tall building with an initial speed of zero. The mass strikes the ground with a downward velocity of 25 m/s. Find the change in mechanical energy of the mass caused by air resistance between the point where it is dropped and the point where it strikes the ground?
a. -0.46 kJ
b. -0.53 kJ
c. -0.61 kJ
d. -0.38 kJ
e. -0.81 kJ
B
You might also like to view...
Conduction: An architect is interested in estimating the rate of heat loss, ?Q/?t, through a sheet of insulating material as a function of the thickness of the sheet. Assuming fixed temperatures on the two faces of the sheet and steady state heat flow, which one of the graphs shown in the figure best represents the rate of heat transfer as a function of the thickness of the insulating sheet? 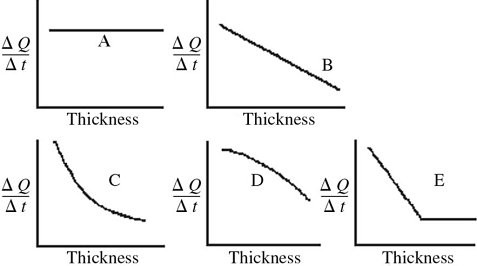
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E
Scientists believe a liquid water ocean might exist on the moon
A. Mimas. B. Europa. C. Titan. D. Triton.
In 1908 there was a huge explosion referred to as the Tunguska event which occurred in Siberia. Apparently this was caused by a very large meteorite, a small asteroid, or a comet colliding with the Earth. If the energy released, estimated at 5 × 10^16 J, were from the kinetic energy of the object, what would have been its approximate mass if its speed had been 104 m/s?
a. 106 kg b. 109 kg c. 1012 kg d. 1014 kg
The size of the electric current in a electrical conductor is a function of which of the following?
a. conductor cross sectional area c. density of charge carriers b. velocity of charge carriers d. All of these choices are valid.