Draw a graph showing the trade-off between salary and benefits. Show an employee's indifference and a firm's isocost curve. Label the equilibrium salary/benefits combination. Discuss what would happen as individual taxes fall or as firm payroll taxes rise.
What will be an ideal response?
The indifference curve "U" shows all salary/benefits combinations that meet the employee's reservation level of utility. The three isocost lines show three different levels of total compensation that the firm could offer. The cost-minimizing offer is (S*, F*). As individual taxes fall, the indifference curve would become flatter since the employee would be willing to trade off a lesser amount of salary for a dollar of benefits. In this case, the equilibrium point would involve more salary and fewer benefits. If payroll taxes rise, the firm incurs a higher cost of salary per dollar paid to the employee. The isocost curves will become flatter, and the equilibrium point will involve less salary and more benefits.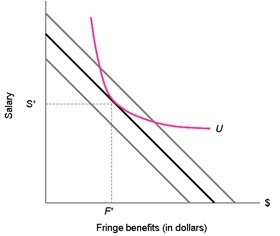
You might also like to view...
Assume that both the demand curve and the supply curve for MP3 players shift to the right but the demand curve shifts more than the supply curve. As a result
A) the equilibrium price of MP3 players will decrease; the equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease. B) the equilibrium price of MP3 players will increase; the equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease. C) the equilibrium price of MP3 players may increase or decrease; the equilibrium quantity will increase. D) both the equilibrium price and quantity of MP3 players will increase.
The Social Security Administration projects that the dependency ratio will
A. rise rapidly over the next 50 years (from around 20% to around 57%). B. remain relatively constant at around 20%. C. rise rapidly over the next 20 years (from around 25% to around 38%), stabilize for 20 years, and then grow again. D. rise rapidly over the next 20 years (from around 25% to around 38%), stabilize for 20 years, and then fall.
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry in an industry?
A. Profit maximization B. Strategic pricing C. Government licensing D. Economies of scale
When someone takes out a mortgage loan to buy a house, the mortgage lender can take possession of the house and sell it if the borrower defaults on the loan because the house is being pledged as ________ for the loan
A) goodwill B) a liability C) insurance D) collateral