Refer to Figure 31-1. The type of larva pictured at #4 is a:
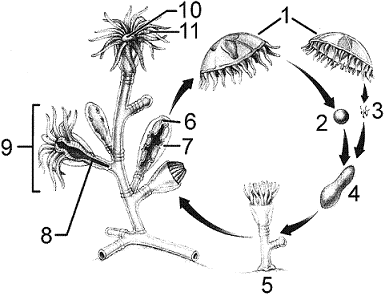
A. planula.
B. miracidium.
C. cercaria.
D. polyp.
E. medusa
A
You might also like to view...
What adjective best describes the risk of being infected with HIV from a blood transfusion?
Starch, dextran, glycogen, and cellulose are polymers of
A) amino acids. B) glucose. C) fatty acids. D) nucleic acids. E) acids
Air is continuously forced through tubes that
thread through vascularized tissue in a pair of inelastic lungs in a. some fish. b. amphibians. c. birds. d. reptiles. e. some small mammals
When a bacterial cell with a chromosome-borne F factor conjugates with another bacterium, how is the transmitted donor DNA incorporated into the recipient's genome?
A) It is substituted for the equivalent portion of the recipient's chromosome by the process of crossing over. B) It circularizes and becomes one of the recipient cell's plasmids. C) Any genes on the donor DNA of which the recipient does not have are added to the recipient chromosome; the remainder of the donor DNA is degraded. D) The donor and recipient DNA are both chopped into segments by restriction enzymes, and a new, composite chromosome is assembled from the fragments.