Figure 11-8
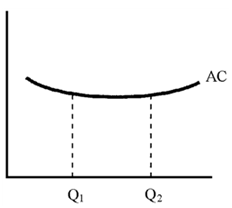
Consider the average cost curve shown in Figure 11-8, for the production of cleaning. If the firm serves the entire market and sells Q1 units. Based upon this information, the firm is experiencing
A. constant returns to scale .
B. increasing returns to scale.
C. decreasing returns to scale.
D. externalities.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
If consumers completely cease purchasing a product when its price increases by any amount, then demand is:
A. unit elastic. B. perfectly inelastic. C. perfectly elastic. D. inelastic.
For a regulated natural monopoly, an average cost pricing rule sets price equal to
A) average fixed cost. B) average total cost. C) average external cost. D) average variable cost.
The above figure shows the marginal benefit from pollution for two firms. If each firm receives a marketable permit to produce 25 units of pollution, which one of the following is most likely to happen?
A) Firm B will sell some pollution rights to firm A. B) Firm A will sell some pollution rights to firm B. C) Firm A will produce all 50 units of pollution. D) Both firms will produce 25 units of pollution.
A tax equal to the external cost on firms that emit pollutants would: a. provide firms with the incentive to increase the level of activity creating the pollution
b. provide firms with the incentive to decrease the level of activity creating the pollution. c. provide firms with little incentive to search for less environmentally damaging production methods. d. not reduce pollution levels at all.