A 6-g lead bullet traveling in 20°C air at 300 m/s strikes a flat steel plate and stops. What is the final temperature of the lead bullet? (Assume the bullet retains all heat.) The melting point of lead is 327°C. The specific heat of lead is 0.128 J/g•°C. The heat of fusion of lead is 24.5 J/g
a. 227°C
c. 293°C
b. 260°C
d. 327°C
D
You might also like to view...
Compared with the speed of light in a vacuum, the speed of light in the empty space between molecules in glass is
A) more. B) the same. C) less.
During an isochoric process, the internal (thermal) energy of a gas decreases by 50 J. How much heat is added to the gas during this process?
A) 50 J B) 25 J C) -50 J D) -25 J E) 0 J
Springs: An ornament of mass 40.0 g is attached to a vertical ideal spring with a force constant (spring constant) of 20.0 N/m. The ornament is then lowered very slowly until the spring stops stretching. How much does the spring stretch?
A. 0.00200 m B. 0.0196 m C. 0.0816 m D. 0.800 m E. 0.200 m
Suppose that an object’s entropy increases from zero when its thermal energy is U = 0 to some maximum value when U = 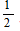 Umax, and then goes back to zero when U = Umax (as shown in the drawing below). The greatest thermal energy U that such an object could have when in thermal equilibrium with a normal object is closest to which of the following?
Umax, and then goes back to zero when U = Umax (as shown in the drawing below). The greatest thermal energy U that such an object could have when in thermal equilibrium with a normal object is closest to which of the following?
A. 0
B. 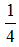 Umax
Umax
C. 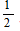 Umax
Umax
D. 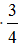 Umax
Umax
E. Umax
F. Other (specify)