The figure below shows the foreign exchange market. D£ is the nonofficial demand curve for pounds. S£ (Spring-summer) and S£ (Autumn-winter) are the nonofficial supply curves of pounds during the spring-summer and autumn-winter seasons, respectively. In the Spring-summer period, what is the social gain if the British government maintains a fixed exchange rate at $1.90 per pound?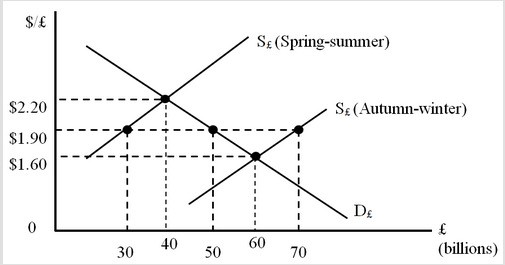
A. 3 billion dollars
B. 3 billion pounds
C. 10 billion pounds
D. 6 billion dollars
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The conventional tools of monetary policy include:
A. the currency-to-deposit ratio. B. the deposit rate. C. the target federal funds rate range. D. both the deposit rate and the target federal funds rate range.
Suppose that Tim is willing to pay $50 for a dozen of roses for Kim on Valentine's Day. If he actually pays $2.50 per rose for the 12 roses, his total consumer surplus is:
A. $50. B. $30. C. $20. D. $12.
Which of the following is true?
A) If the income elasticity of demand f is greater than 0, then the good is labeled as inferior. B) The law of diminishing marginal utility states that utility declines as more of a good is consumed. C) The law of demand states that as the price of a commodity rises, the changes in consumer surplus is negative. D) If the cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods is negative, then the two goods are complements.
Which of the following did not contribute to the overall decline in death rates in the United States since 1981?
A) a decline in smoking B) the decline in the population C) the availability of new prescription drugs D) new surgical techniques