Use the following graph for a perfectly competitive firm to answer the next question.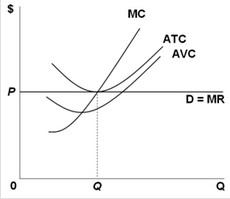 At its short-run equilibrium point, the firm's
At its short-run equilibrium point, the firm's
A. marginal revenue equals its average variable cost.
B. marginal cost equals its average fixed cost.
C. marginal revenue equals its average total cost.
D. marginal cost equals its average variable cost.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If you bought a long contract on financial futures you hope that interest rates
A) rise. B) fall. C) are stable. D) fluctuate.
To earn an economic profit in the short-run, a monopolist sets marginal revenue equal to zero
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
As a result of a kinked demand curve, the price:
a. fluctuates. b. falls below the kink. c. settles at the kink. d. rises above the kink.
Refer to the following graphs. Given an increase in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2, which of the following statements is true?
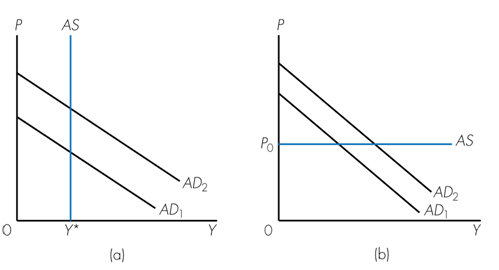
a. Classical economists argue the Aggregate Supply (AS) curve would be vertical like that shown in graph (a).
b. Keynesian economists argue the Aggregate Supply (AS) curve would be horizontal in the short run like that shown in graph (b).
c. Keynesian economists argue the Aggregate Supply (AS) curve would be vertical in the long run like that shown in graph (a).
d. All of the above.