Suppose an investor purchased 100 shares of JDSU stock at a price of $50 per share on December 31, 2011. On December 31, 2012, JDSU paid dividends of $1.50 per share, and the investor received the dividends, then sold the stock at a price of $65 per share.
a.If there were no taxes or inflation, what was the total return? b.If there were no taxes, but inflation was 3.5 percent, what was the real return? c.If the tax rate was 15 percent on dividends and capital gains, what was the after-tax real return?
What will be an ideal response?
| a. | Income = dividends + capital gains = $1.50 + ($65 ? $50) = $16.50 | |
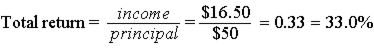 | ||
| b. | Loss of principal value to inflation | = inflation rate × principal value |
| = 0.035 × $50 = $1.75 | ||
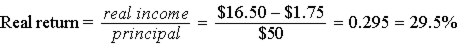 | ||
| c. | Taxes | = (0.15 × dividends) + (0.15 × capital gains) |
| = (0.15 × $1.50) + (0.15 × $15) | ||
| = $0.225 + $2.25 | ||
| = $2.475 | ||
| After-tax real income = $16.50 ? $1.75 ? $2.475 = $12.275 | ||
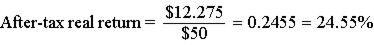 | ||
You might also like to view...
________ involves a manipulation of scale values to ensure comparability with other scales or otherwise make the data suitable for analysis
A) Standardization B) Variable respecification C) Scale transformation D) Weighting
For the year ended December 31, Year 1, Carsem Company had cash collections from customers of $220,000, cash paid to employees of $32,000, cash paid to suppliers of $100,000, cash used to retire long-term bonds of $32,000, and cash payments for dividends of $20,000. Based on this information, what is the net cash provided from operating activities?
A. $68,000 B. $188,000 C. $120,000 D. $88,000
A short-term investment in a U.S. Treasury bill costs $24,400 and will mature six months later at $25,000. Management intends to hold the investment until it matures. The entry to record the initial investment is:
A) Short-Term Investments 25,000 Cash 25,000 B) Cash 24,400 Short-Term Investments 24,400 C) Short-Term Investments 24,400 Cash 24,400 D) Cash 25,000 Short-Term Investments 24,400Interest Income 600
Systems Inc. went through a downsizing process. The company decentralized its distribution of power to its employees while creating teams. Each of the departments was left with a range of seven to fifteen people who worked collectively to create new ideas. Management was behind this plan, but found the new approach caused more headaches than benefits. The teams were not productive. What was Systems Inc.’s downfall?
a. Systems Inc. had groups that were not working well together b. Systems Inc. had too many teams c. Systems Inc. had too many groups d. Systems Inc. had too many people in their teams.