Many companies have to monitor some of their financial statement ratios, such as the current ratio, due to debt covenants. Selected transactions are provided below for a company that uses a perpetual inventory system; sells its merchandise at a selling price that exceeds cost; and had a current ratio of 1.85 to 1 before the event occurred. Required:In the above table, indicate whether each transaction would increase (+), decrease (?), or not affect (0) the company's working capital and the current ratio.
Required:In the above table, indicate whether each transaction would increase (+), decrease (?), or not affect (0) the company's working capital and the current ratio.
What will be an ideal response?
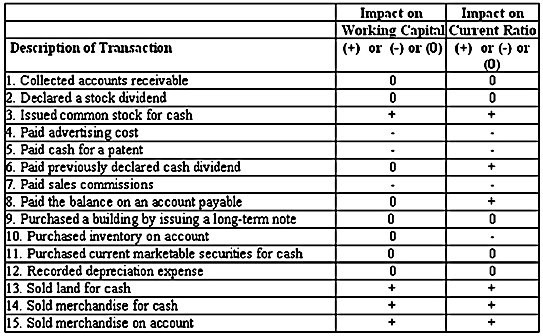
Working capital = Current assets ? Current liabilities
Current ratio = Current assets ÷ Current liabilities
Impact of each transaction on these components:
1) No change in current assets (since increase in cash equals decrease in accounts receivable) and no change in current liabilities
2) No change in current assets or current liabilities
3) Increase in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
4) Decrease in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
5) Decrease in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
6) Decrease in current assets (cash) and decrease in current liabilities (dividends payable).
To determine the impact on the current ratio, assume that the current ratio of 1.85 to 1
meant that current assets were $185,000 and current liabilities were $100,000 and the
dividend payment was for $10,000. The new current ratio would then equal ($185,000 ? $10,000) ÷ ($100,000 ? $10,000) = $175,000 ÷ $90,000 = 1.94 (which is an increase from 1.85 to 1).
7) Decrease in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
8) Decrease in current assets (cash) and decrease in current liabilities (accounts payable)
To determine the impact on the current ratio, assume that the current ratio of 1.85 to 1 meant that current assets were $185,000 and current liabilities were $100,000 and the payment on account was for $10,000. The new current ratio would then equal ($185,000 ? $10,000) ÷ ($100,000 ? $10,000) = $175,000 ÷ $90,000 = 1.94 (which is an increase from 1.85 to 1).
9) No change in current assets or current liabilities
10) No change in current assets (inventory) and increase in current liabilities (accounts payable)
11) No change in current assets (since increase in cash equals decrease in current marketable securities) and no change in current liabilities
12) No change in current assets or current liabilities
13) Increase in current assets (cash) and no change in current liabilities
14) Increase in current assets (since increase in cash exceeds decrease in inventory) and no change in current liabilities
15) Increase in current assets (since increase in account receivable exceeds decrease in inventory) and no change in current liabilities
You might also like to view...
In the context of American business, which of the following statements is true of the changing scenario of operations management over the last five decades?
A. The nonfarm labor force is increasingly joining the goods-producing sector. B. The current trend in value chain design is to rely more on vertical integration and less on outsourcing and offshoring. C. There has been a shift from mass customization to mass production. D. There has been a fundamental shift away from the production of goods and toward the provision of services.
On February 15, Jewel Company buys 7,000 shares of Marcelo Corp. common stock at $28.53 per share plus a brokerage fee of $400. The stock is classified as available-for-sale securities. This is the company's first and only investment in available-for-sale securities. On March 15, Marcelo Corp. declares a dividend of $1.15 per share payable to stockholders of record on April 15. Jewel Company received the dividend on April 15 and ultimately sells half of the Marcelo Corp. stock on November 17 of the current year for $29.30 per share less a brokerage fee of $250. The journal entry to record the dividend on April 15 is:
A. Debit Cash $7,350; credit Interest Revenue $7,350. B. Debit Cash $8,050; credit Gain on Sale of Investments $8,050. C. Debit Cash $8,050; credit Interest Revenue $8,050. D. Debit Cash $7,350; credit Dividend Revenue $7,350. E. Debit Cash $8,050; credit Dividend Revenue $8,050.
The most important part of the Constitution with respect to businesses is:
a. the commerce clause b. the business clause c. the trade clause d. the mercantile clause e. the money clause
Which of the following combines a series of small tasks into one, new broader job so that people perform a variety of activities?
A. Job simplification B. Job rotation C. Job enrichment D. All of these E. None of these