Refer to the graph shown. A movement from D to C is most likely to be caused by: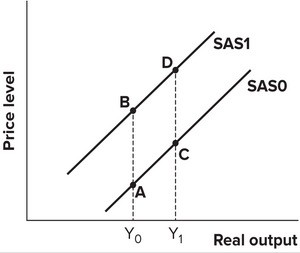
A. an increase in aggregate demand.
B. an increase in input prices.
C. a reduction in sales taxes.
D. an increase in import prices.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A, and the government initiates an expansionary monetary policy to increase aggregate demand
Which of the following is a TRUE statement concerning the differences between what happens when the central bank action is unanticipated and when it is anticipated? A) The new long-run equilibrium will be point C in either case. When the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated, the economy moves to B in the short run, but when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated, short-run aggregate supply shifts when the aggregate demand curve shifts, and the economy moves immediately to point C. B) The new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated is point B while the new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated is point C. C) The new long-run equilibrium is point C in either case. When the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated, the new short-run equilibrium is point B, but when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated the new short-run equilibrium is point D. D) The new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is unanticipated is point B while the new long-run equilibrium when the increase in aggregate demand is anticipated is point A.
Which of the following would cause both the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of oysters (assume that oysters are a normal good) to decrease?
A) an oil spill that sharply reduces oyster output B) a decrease in consumer income C) a technological advancement in the production of oysters D) an increase in consumer income
Fiscal policy formation causes a delay in implementation even though a recession can usually be recognized within a few weeks after it begins.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Which of the following is FALSE regarding bilateral monopoly?
A. The price outcome is easily determined. B. Bilateral monopoly is defined as a market structure in which a single buyer faces a single seller. C. An example of bilateral monopoly is a state education employer facing a single teachers' union in the labor market. D. Bilateral monopoly is a market structure consisting of a monopolist and a monopsonist.