Under a system of marketable pollution permits:
A. firms can trade away their right to pollute.
B. the amount of pollution an individual firm can generate is determined by the number of permits issued to it by the government.
C. the production costs for firms are not affected.
D. the government controls the production process of firms who pollute.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
In a competitive industry, each firm has a cost function 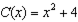
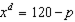
A. 120 B. 58 C. 46 D. 34 E. 29 F. 12 G. 2 H. None of the above
It would always be a mistake to view
a. a streetlight as a common resource. b. a nontoll road as a public good. c. the environment as a common resource. d. a lighthouse as a public good.
Assume peanut butter and jelly are complements. Ceteris paribus, an increase in the price of peanut butter will cause the equilibrium price of jelly to
A. Decrease and the equilibrium quantity of jelly to decrease. B. Increase and the equilibrium quantity of jelly to decrease. C. Decrease and the equilibrium quantity of jelly to increase. D. Increase and the equilibrium quantity of jelly to increase.
Refer to the consumption schedule above. If disposable income is $42,000, then saving is:
$4,000 $2,000 $0 $6,000