Games can be judged according to the payoffs
A) as zero-sum, negative-sum, and positive-sum games.
B) as collusive or noncollusive games.
C) as competitive or noncompetitive games.
D) whether all companies participate or not.
A
You might also like to view...
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 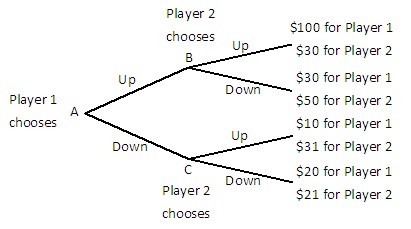 Suppose Player 1 and Player 2 enter into a binding agreement in which Player 1 agrees to pay Player 2 a fixed amount of money to get Player 2 to play Up when it is Player 2's turn. How much will Player 1 have to pay Player 2 to get Player 2 to play Up?
Suppose Player 1 and Player 2 enter into a binding agreement in which Player 1 agrees to pay Player 2 a fixed amount of money to get Player 2 to play Up when it is Player 2's turn. How much will Player 1 have to pay Player 2 to get Player 2 to play Up?
A. at least $20. B. at least $50. C. at least $10. D. $0
Markets can fail to achieve efficiency when
a. there are prices consumers do not think are fair. b. there are wages workers do not think are fair. c. trade puts people out of work. d. there are buyers or sellers without adequate information about the quality of goods.
Fiscal policy is
a. a change in money supply designed to change total spending. b. a change in interest rates designed to change total spending. c. a change in government purchases or net taxes designed to change total spending. d. a change in government regulations designed to change total spending. e. a change in policy stance by the Federal Reserve designed to change total spending.
Which statement is TRUE? Fixed costs
A) do NOT exist in the long run. B) depend on the firm's level of output. C) are zero if the firm is producing nothing. D) are the difference between total costs and average variable costs.