Did the terminal window that was already open also change color from green to red? Explain.
Editing and Saving Configuration files
Let’s edit .bashrc to change the color of the shell prompt from green to red for the analyst user.
a. First, open SciTE by selecting Applications > CyberOPS > SciTE from the tool bar located in the upper portion of the Cisco CyberOPS VM screen.
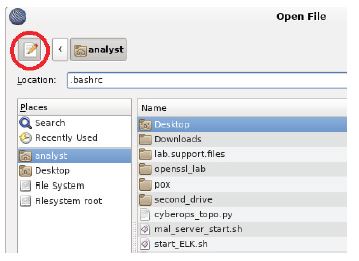
b. Select File > Open to launch SciTE’s Open File window.
c. Because .bashrc is a hidden file with no extension, SciTE does not display it in the file list. If the Location feature is not visible in the dialog box, click the Type a filename button, as shown below, and type .bashrc. Click Open.
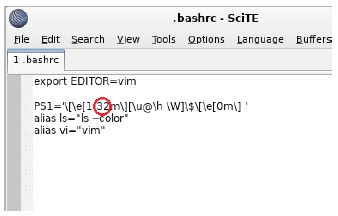
d. Locate 32 and replace it with 31. 32 is the color code for green, while 31 represents red.
e. Save the file by selecting File > Save and close SciTE by clicking the X icon.
f. Click the Terminal application icon located on the Dock, at the bottom center of the Cisco CyberOPS V M screen. The prompt should appear in red instead of green.
No. The .bashrc file is executed and applied when a terminal is first opened, so any previously
opened terminals will be unaffected by the changes to the .bashrc file.
You might also like to view...
When a derived class constructor calls its base class constructor, what happens if the base class’s constructor does not assign a value to one of its instance variables?
a. a syntax error occurs b. a compile-time error occurs c. a run-time error occurs d. the instance variables are initialized to their default values
Create a directory called linux in your home directory. What command line did you use? What command would you use to create the directories called memos and personal in your home directory?
What will be an ideal response?
If the ADT queue had a method clearthat removed all entries from a queue,what would its definition be in the previous array-based implementation?
What will be an ideal response?
_____ is a measure of the average time from the point at which customers enter the queue until the moment they leave the server.
A. Response time B. Serve time C. Queue time D. Processing time