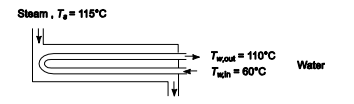
In an industrial plant a shell-and-tube heat exchanger is heating pressurized dirty water at the rate of 38 kg/s from 60 to 110°C by means of steam condensing at 115°C on the outside of the tubes. The heat exchanger has 500 steel tubes (ID = 1.6 cm, OD = 2.1 cm) in a tube bundle which is 9-m-long. The water flows through the tubes while the steam condenses in the shell. If it may be assumed that the thermal resistance of the scale on the inside pipe wall is unaltered when the mass rate of flow is increased and that changes in water properties with temperature are negligible, estimate (a) the heat transfer coefficient on the water side and (b) the exit temperature of the dirty water if its mass rate of flow is doubled.
GIVEN
? Shell-and-tube heat exchanger - dirty water in steel tubes, steam condensing in shell
? Water flow rate
( mw ) = 38 kg/s
? Water temperatures
? Tw,in = 60°C
? Tw,out = 110°C
? Steam temperature (Ts) = 115°C
? Number of tubes (N) = 500
? Tube diameters
? Di = 1.6 cm = 0.016 m
? Do = 2.1 cm = 0.021 m
? Tube bundle length (L) = 9 m
FIND
(a) The heat transfer coefficient on the water side
( hi )
(b) The exit temperature of the dirty water (Tw,out) if the mass flow rate
( mw FIND
(a) The heat transfer coefficient on the water side
( ) hi
(b) The exit temperature of the dirty water (Tw,out) if the mass flow rate
( mw ) is double
ASSUMPTIONS
? The thermal resistance of the scale in the pipe is unaltered when the mass flow rate is increased
? Changes in water properties with temperature are negligible
? Two, or a multiple of two, passes
? The dirty water has the same thermal properties as clean water
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 13, for water at the average temperature of 85°C
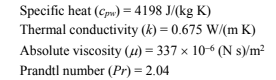
From Appendix 2, Table 10, the thermal conductivity of 1% carbon steel (ks) = 43 W/(m K) (at 20°C)
(a) The Reynolds number for flow in the tubes is

Applying Equation (7.61) for turbulent flow in tubes

(b) The scaling resistance can be calculated from the water temperature data
From Figure (10.10)
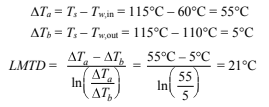
This must be corrected for use in a shell-and-tube heat exchanger according to Figure 10.14. But since Z = 0 for condensers, F = 1 and ?Tmean = LMTD, the rate of heat transfer is
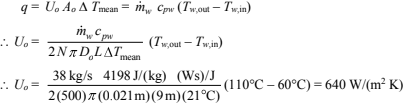
Applying Equation (10.6) (Ro = 0)
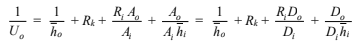
Solving for the sum of the scaling, conductive, and outer convective resistances
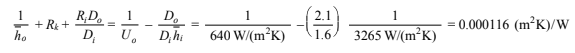
For a double flow rate, the Reynolds number is doubled: ReD = 35,592
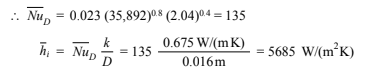
The new overall heat transfer coefficient is
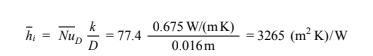
From Figure 10.20, e = 1
From Equation (10.13b)
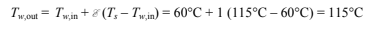
You might also like to view...
What is the lifetime of a 10-solar-mass star on the main sequence?
a. 3.2 × 10^7 years
b. 320 years
c. 3.2 × 10^12 years
d. 1× 10^9 years
e. 1 × 10^11 years
A ‘cliff diver' in Mexico dives off a high cliff and falls for 2.3 seconds before hitting the water. (a) How fast is the diver going at impact? (b) How far below the cliff is the diver at this point?
A disk has a moment of inertia of 3.0 × 10^-4 kg•m2 and rotates with an angular speed of 3.5 rad/sec. What net torque must be applied to bring it to rest within 3.7 s?
a. 4.6 × 10^-4 N•m c. 3.5 × 10^-4 N•m b. 7.5 × 10^-4 N•m d. 2.8 × 10^-4 N•m
Intensity: A radio transmitter is operating at an average power of 4.00 kW and is radiating uniformly in all directions. What is the average intensity of the signal 8.00 km from the transmitter?
A. 4.97 ?W/m2 B. 2.49 ?W/m2 C. 0.00497 W/m2 D. 0.00249 W/m2