The choice between futures and options
A) depends on whether the underlying instrument is a debt instrument or an equity.
B) reflects a trade-off between the higher cost of using options and the extra insurance benefits that options provide.
C) reflects a trade-off between the higher cost of using futures and the extra insurance benefits that futures provide.
D) reflects a trade-off between the greater risk from using options and the extra insurance benefits that options provide.
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 16-6. In the dynamic model of AD-AS in the figure above, if the economy is at point A in year 1 and is expected to go to point B in year 2, and no fiscal or monetary policy is pursued, then at point B
A) the unemployment rate is very low. B) there is pressure on wages and prices to fall. C) income and profits are falling. D) firms are operating at below capacity. E) the economy is below full employment.
Which of the following items is included in the calculation of GDP?
a. Purchase of 100 shares of General Motors stock. b. Purchase of a used car. c. The value of a homemaker's services. d. Sale of Gulf War military surplus. e. None of these would be included.
Suppose that electricity producers create a negative externality equal to $5 per unit. Further suppose that the government imposes a $5 per-unit tax on the producers. What is the relationship between the after-tax equilibrium quantity and the socially optimal quantity of electricity to be produced?
a. They are equal. b. The after-tax equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity. c. The after-tax equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity. d. There is not enough information to answer the question.
A firm is experiencing theft problems at its warehouse. A consultant to the firm believes that the dollar loss from theft each week (T) depends on the number of security guards (G) and on the unemployment rate in the county where the warehouse is located (U measured as a percent). In order to test this hypothesis, the consultant estimated the regression equation T = a + bG + cU and obtained the following results: 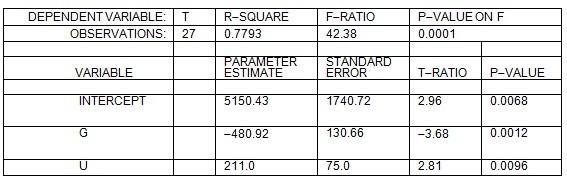 Based on the above information, if the firm hires 6 guards and the unemployment rate in the county is 10% (U = 10), what is the predicted dollar loss to theft per week?
Based on the above information, if the firm hires 6 guards and the unemployment rate in the county is 10% (U = 10), what is the predicted dollar loss to theft per week?
A. $8,300 per week B. $5,150 per week C. $9,955 per week D. $4,375 per week