What is the basic difference between the short run and long run as these terms relate to macroeconomics? Why does this difference occur?
What will be an ideal response?
The short run is a period in which nominal wages (and other input prices) do not fully adjust as the price level changes. The long run is a period in which nominal wages are fully responsive to changes in the price level. Nominal wages tend to remain fixed in the short run as the price level increases because workers may not be fully aware of how inflation has eroded real wages. Also many workers are under fixed contracts for several year periods. As a consequence of these factors, nominal wages do not change immediately with changes in the price level.
You might also like to view...
What would happen to the budget line if income increases by the same percentage as the price of the two goods decreases (that is income up by, say, 10 percent and the prices down by 10 percent)?
A. A rightward parallel shift in the budget line B. A leftward parallel shift in the budget line C. An upward pivot of the budget line D. The budget line is unaffected
If a supply curve is a horizontal line, supply is said to be
A) unit elastic. B) inelastic. C) perfectly elastic. D) perfectly inelastic.
The figure below shows the supply and demand curves for jeans in Smallville.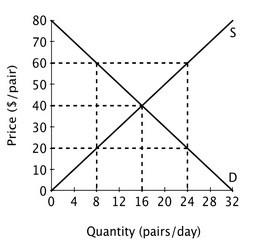 At a price of $60 per pair, there will be an excess ________ of ________ pairs of jeans per day.
At a price of $60 per pair, there will be an excess ________ of ________ pairs of jeans per day.
A. supply; 16 B. supply; 24 C. demand; 8 D. demand; 16
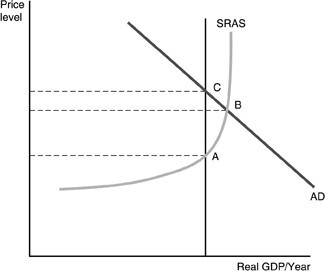 Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy had been at point A and now is at B. What could have caused the movement to B?
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy had been at point A and now is at B. What could have caused the movement to B?
A. Both the labor force and the population increased. B. Winter storms cause factories in the north to be shut down for several weeks. C. Unusually good weather causes the wheat crop to be larger than normal. D. Government spending increased causing aggregate demand to increase.