Use mathematical induction to prove the following.6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6n = 3n(n + 1)
What will be an ideal response?
Answers may vary. One possibility:
Sn: 6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6n = 3n(n + 1)
S1: 6 = 3 ? 1 ? (1 + 1)
Sk: 6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k = 3k(k + 1)
Sk+1: 6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k + 6(k + 1) = 3(k + 1)(k + 2)
Step 1: Since 3 ? 1 ? (1 + 1) = 3 ? 2 = 6, S1 is true.
Step 2: Let k be any natural number. Assume Sk. Deduce Sk+1.
6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k = 3k(k + 1) By Sk
6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k + 6(k + 1) = 3k(k + 1) + 6(k + 1) Adding 6(k + 1)
6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k + 6(k + 1) = (3k + 6)(k + 1) Distributive law
6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k + 6(k + 1) = 3(k + 2)(k + 1)
6 + 12 + 18 + . . . + 6k + 6(k + 1) = 3(k + 1)(k + 2).
You might also like to view...
Simplify.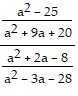
A. 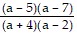
B. 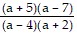
C. 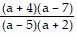
D. 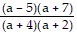
Multiply in the indicated base.
A. 1222four B. 122four C. 1202four D. 1220four
Find the exact value of the expression.sin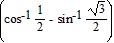
A. 1
B. 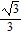
C. 0
D. 
Fill in the blank with one of the words or phrases listed below. Fractions that represent the same portion of a whole are called
Fractions that represent the same portion of a whole are called  fractions.
fractions.
A. equivalent B. prime number C. mixed number D. simplified