Assume that the central bank purchases government securities in the open market. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and current international transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index falls, and current international transactions become more negative (or less positive).
b. The GDP Price Index and current international transactions remain the same.
c. The GDP Price Index rises, and current international transactions remain the same.
d. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
e. The GDP Price Index rises, and current international transactions become more positive (or less negative).
.E
You might also like to view...
The use of seat belts and other automobile safety features making bicycling more hazardous can be explained by the economic concept known as
A) the principle of diminishing returns. B) the principle of voluntary exchange. C) the real-nominal principle. D) the marginal principle.
What is an example of the bidder's curse?
A) addiction to auctions B) paying less than the auctioned good value C) Bid a value that is higher than the price of the good at a retail store. D) Never win an auction.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.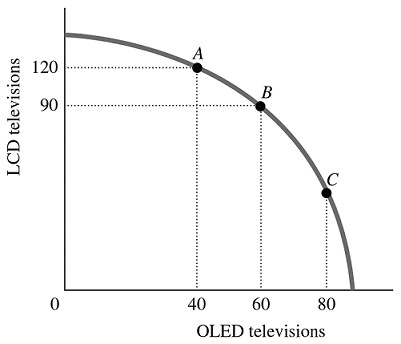 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The best point for society would be
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The best point for society would be
A. either Point B or Point C, as the total amount being produced at either of these points is approximately the same. B. at any of the labeled points, as all of the points represent an efficient allocation of resources. C. Point C, as at this point there are approximately equal amounts of LCD and OLED televisions being produced. D. indeterminate from this information, as we don't have any information about the society's desires.
Are countries that began modern economic growth more recently doomed to be permanently poorer than the countries that began modern economic growth in earlier periods? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?