A stainless steel cylindrical rod with a diameter D = 18 mm and length L = 110 mm is insulated on its exterior surface except for the ends. The mass of the rod is 0.221 kg. The steady one-dimensional temperature distribution in the rod is T(x) = 310?K ? 20?K?(x/L). Determine the heat flux along the rod.
What will be an ideal response?
Diameter, length, and mass of stainless steel rod is given. The rod is insulated on its exterior surface except for the ends. Temperature distribution in the rod is also given. The heat flux along the rod is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Heat conduction is steady and one-dimensional in the x-direction. 2 Thermal conductivity is constant.
Analysis The heat flux can be found from Fourier’s law
q = -k dT/dx
Table A-3 gives values for the thermal conductivity of stainless steels, however we are not told which type of stainless steel the rod is made of, and the thermal conductivity varies between them. We do know the mass of the rod, and can use this to calculate its density:
From Table A-3, with p 7900 kg/m3, it appears that the material is AISI 304 stainless steel. The temperature of the rod from the given equation for temperature distribution varies from 310 K at x = 0 to 290 K at x = L = 110 mm. Evaluating the thermal conductivity at the average temperature of 300 K, from Table A-3, k = 14.9 W/m•K. Thus,
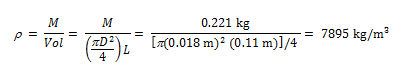
Discussion If the temperature of the rod varies significantly along its length, the thermal conductivity will vary along the rod as much or more than the variation in thermal conductivities between the different stainless steels.
You might also like to view...
What is the main physiological process affected by abscisic acid?
What will be an ideal response?
Technician A says that an engine malfunction on a Mack electronic engine manufactured between 2002 and 2010 can have up to 10 possible causes. Technician B says that an electronic engine malfunction on a post-2010 Mack engine can have up to 25 possible causes. Who is correct?
A. Technician A only B. Technician B only C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B
What are the main components of a wound-rotor induction motor?
What will be an ideal response?
The force required to deploy a typical airbag is approximately equal to the force of a vehicle hitting a wall at over ________ miles per hour
A) 15-10 B) 10 C) 3-5 D) 15