If this is an open economy, the price of a car will be ________. 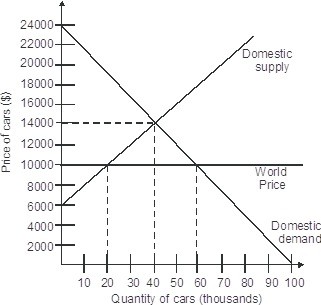
A. $8,000/car
B. $6,000/car
C. $10,000/car
D. $14,000/car
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Compare two situations. (A ) A firm is not legally responsible for damages that result from air pollution caused by its production of steel. (B ) A firm is legally responsible for damages that result from its production of steel
Ronald Coase argued that if the property rights are assigned and transactions costs are low A) bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to an equal reduction in pollution in situation (A ) and situation (B ). B) bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to a greater reduction in pollution in situation (A ) than situation (B ). C) bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to a smaller reduction in pollution in situation (A ) than situation (B ). D) bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm will result in little reduction of pollution in either situation (A ) or (B ) because the firm has greater economic and political power than the victims.
An HVAC company is selling heating and cooling equipment. Between its sales staff and the VP of Marketing, the sales staff would want to
a. Price aggressively to ensure sales are made b. Price less aggressively to ensure that profitable sales are made c. Price at cost to minimize sales d. None of the above
According to the table shown, the firm's marginal revenue:
This table shows the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
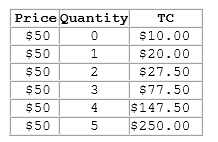
A. is constant.
B. increases as output increases.
C. decreases as output increases.
D. increases until the 3rd unit, then decreases.
Given an upward sloping aggregate supply curve, which of the following changes in the aggregate demand curve is observed when the Fed reduces the money supply?
a. The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward, lowering real GDP and the price level b. The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward, raising real GDP and the price level. c. The aggregate demand curve shifts leftward, lowering real GDP but raising the price level. d. The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward, raising real GDP and the price level. e. The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward, lowering real GDP but raising the price level.