Assuming no crowding-out, investment-accelerator, or multiplier effects, a $100 billion increase in government expenditures shifts aggregate demand
a. right by more than $100 billion.
b. right by $100 billion.
c. left by more than $100 billion.
d. left by $100 billion.
b
You might also like to view...
Explain the difference between U.S. GDP and U.S. GNP
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the figure above. If the monopolist faces a constant marginal cost of $10, at what price should it sell its output?
A) $2 B) $10 C) $12 D) $14
Relative to an environment with free trade and no tariff, the winners from the tariff are the domestic ________, and the losers from the tariff are the domestic ________.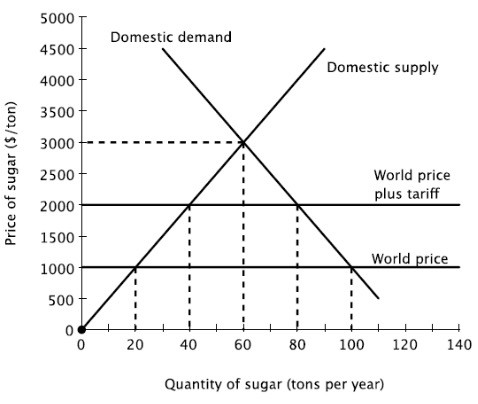
A. producers of sugar and the government; consumers of sugar B. producers of sugar; consumers of sugar and the government C. consumers of sugar and the government; producers of sugar D. consumers of sugar; producers of sugar
Rents
A. have no useful economic purpose. B. have a distributional function since they affect incomes, but have no allocative function since the resource is in fixed supply. C. have an allocative function since they help decide to which use a resource will be put. D. have an economic purpose only if they are taxed and provide revenue to the government.