Why does sexual reproduction produce more genetic variability in a population than asexual reproduction?
A. Sexually reproducing organisms mutate more rapidly during DNA replication than asexually reproducing organisms.
B. Sexually reproducing organisms mix parental genetics in addition to crossing-over and random alignment.
C. Organisms arising from sexual reproduction can change their genetic material in response to environmental changes.
D. In sexual reproduction, the parents exchange genetic material of the nuclei, thus increasing their variability.
E. Offspring are identical to one parent, when produced through sexual reproduction.
B. Sexually reproducing organisms mix parental genetics in addition to crossing-over and random alignment.
You might also like to view...
The existence of discrete variants of a particular character is known as ____
a. homozygous dominance b. a quantitative trait c. genotypic variation d. a polymorphism e. genetic equilibrium
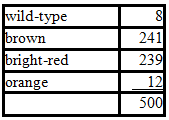
What is the map distance between the pr and cn genes?
In Drosophila, the autosomal recessive pr and cn mutations cause brown and bright-red eyes, respectively (wild-type flies have brick-red eyes). Flies who are homozygous recessive at both pr and cn have orange eyes. A female who has wild-type eyes is crossed to an orange-eyed male. Their progeny have the following distribution of eye colors:
A) 20 m.u.
B) 2 m.u.
C) 4 m.u.
D) 46 m.u.
E) 8 m.u.
Syndrome means
a. a chromosome disorder. b. a simple genetic disease. c. a set of symptoms that occur together. d. an incurable disease. e. a rare inborn defect.
The advantages of DNA vaccines include
a. no possibility of infection. b. activation of T and B cells. c. targeted immune response. d. all of the above.