What are the assumptions of a pure monopoly?
What will be an ideal response?
One producer, no close substitutes, barriers to entry.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the above figure. The long-run average cost curve and the long-run marginal cost curves represent
A) the cost curves for a competitive firm. B) the cost curves for a natural monopoly. C) a situation where a firm has control over the raw materials. D) a situation where a firm has a patent.
Under which one of the following situations would you be better off?
A) You have $10,000 in your savings account paying 5 percent per year and unanticipated inflation is 8 percent per year. B) You have paid $500 for a $1,000 U.S. savings bond that matures in 10 years and unanticipated inflation is 10 percent per year. C) You lend a friend $1,000 at 6 percent to be repaid in one year and unanticipated inflation is 7 percent during the year. D) You borrowed $2,500 at 7 percent to pay for this year's college expenses and unanticipated inflation is 12 percent during the year.
The breakeven price of a perfectly competitive firm is obtained at the point of intersection between the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.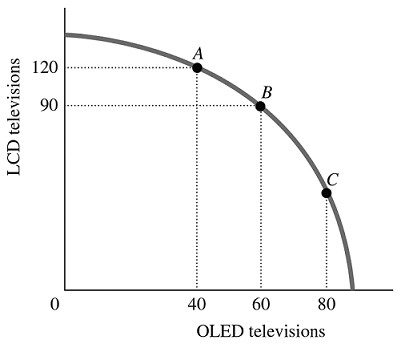 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
A. 120 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED TVs. B. 30 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED TVs. C. 20 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 30 additional LCD TVs. D. 40 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 120 additional LCD TVs.