Monopolistically competitive firms:
A. earn zero economic profits in both the short run and the long run.
B. can earn economic profits or losses in both the short run and the long run.
C. earn economic profits in the short run but zero economic profits in the long run.
D. can earn either profits or losses in the short run but earn zero economic profits in the long run.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Constantine purchased 100 shares of IBM stock several years ago for $150 per share. The price of these shares has fallen to $55 per share. Constantine's investment strategy is "buy low, sell high"
Therefore, he will not sell his IBM stock until the price rises above $150 per share. If he sells at a price lower than $150 per share he will have "bought high and sold low." Constantine's decision: A) is correct and shows a solid command of the nature of opportunity cost. B) is incorrect because the original price paid for the shares is a sunk cost and should have no bearing on whether the shares should be held or sold. C) is incorrect because when the price of a stock falls, the law of demand states that he should buy more shares. D) is incorrect because it treats the price of the shares as an explicit cost.
When a government splits a natural monopoly vertically, it is breaking the company up:
A. along its stages of production. B. into smaller companies providing the same goods. C. in order to maximize its profits. D. in order to capture all efficiencies possible.
A price floor establishes a minimum price, and a price ceiling establishes a maximum price
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the figure below. What is the price elasticity of demand when the price of rice is $3 per pound? 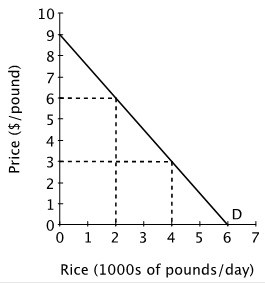
A. 2 B. 0.5 C. 0.75 D. 0.67