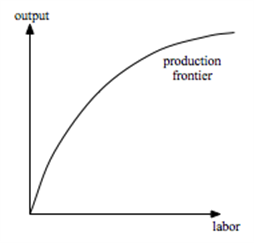
Suppose a price-taking firm uses a single input - labor - to produce an output x. The production technology has diminishing marginal product of labor throughout.
a. On a graph with labor hours on the horizontal and output on the vertical axis, illustrate the production frontier for this firm.
b. For a given wage rate w and output price p, illustrate three isoprofit curves corresponding to profit levels ?
What will be an ideal response?
b. At the profit maximizing production plan A,
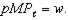
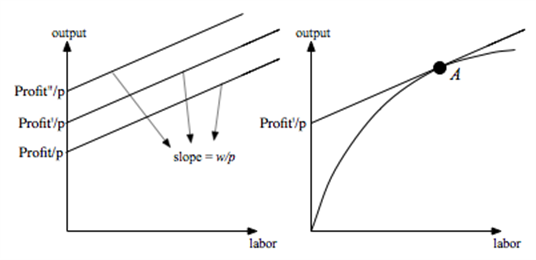
c. All production plans that lie on the production frontier are cost-minimizing.
d. e.
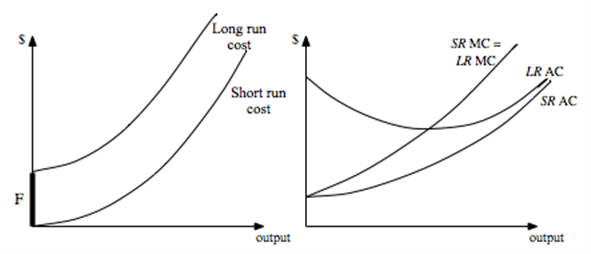
f. The short-run supply curve is the entire MC curve --- including the dashed and solid parts below. The long run supply curve is just the solid part that lies above the long run AC curve.
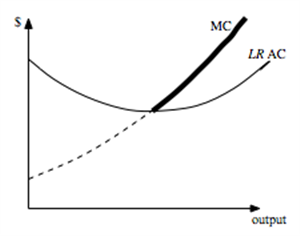
g. Yes, because the long run equilibrium price is determined by the lowest point of the marginal firm's long run AC curve -- which is the same for firms in both industries.
h. The number went down in industry A and up in industry B -- because the quantity demanded falls more in industry A than in industry B. Firms therefore exit industry A and enter industry B.
You might also like to view...
Suppose Bob leaves his $50,000-a-year job as a financial advisor to P.E.T.S. and starts his own business selling spot remover for Dalmatians. In the first year his accounting profit is $70,000 . Based on this level of success, Bob should
a. return to his old job because his economic profit is negative b. return to his old job because his economic profit is smaller than his accounting profit c. return to his old job because his economic profit is less than his old salary d. stay with his new firm because his economic profit is positive e. stay with his new firm because accounting profit is positive
By comparing the value of marginal product with the marginal cost per input, a firm can find the:
A. cost-maximizing quantity to hire. B. profit-maximizing quantity to hire. C. revenue-maximizing quantity to hire. D. output-maximizing quantity to hire.
When price is $2
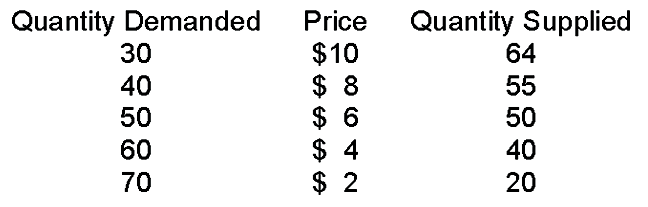
A. there is a surplus.
B. there is a shortage.
C. quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied.
D. price must fall to get to equilibrium.
According to purchasing-power parity, which of the following necessarily equals the ratio of the foreign price level divided by the domestic price level?
a. the real exchange rate, but not the nominal exchange rate b. the nominal exchange rate, but not the real exchange rate c. the real exchange rate and the nominal exchange rate d. neither the real exchange rate nor the nominal exchange rate