In the Keynesian model, when is the economy in short-run equilibrium?
a. when there is no inflation
b. when there is full employment
c. when there is a balanced federal budget
d. when total spending (demand) is equal to production (supply)
Ans: d. when total spending (demand) is equal to production (supply)
You might also like to view...
Decisions to determine the government's budget are called:
A. fiscal policy. B. structural policy. C. trade policy. D. monetary policy.
Refer to Table 6-5. Katie Graham owns a kayak rental service in Santa Barbara. Table 6.5 shows her estimated demand schedule for kayak rentals per week. She would like to increase her sales revenue by changing the price she charges for rentals
At present she charges $75. Based on the information in the table, Katie A) should raise her price to $80 to increase her revenue because the demand for kayak rentals is price inelastic. B) should raise her price to earn the most revenue. C) should lower her price to $60 to increase her revenue because the demand for kayak rentals is price elastic. D) is not able to increase her revenue by changing her price because the demand for kayak rentals is unit elastic.
Refer to the following graph. Which of the following statements is true?
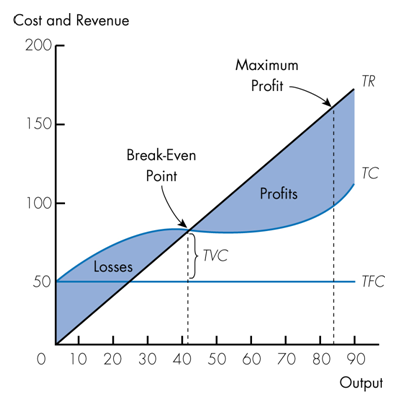
a. When output is zero losses equal TFC.
b. At the Break-Even Point marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
c. Any output below the Break-Even Point indicates profits are earned.
d. When Total Revenue equals Total Cost profits are maximized.
If wealthy U.S. consumers save most of their tax cut, this means that, compared to government spending changes,
a. tax changes would have a higher multiplier effect. b. tax changes would have a weaker multiplier effect. c. government spending would have a weaker multiplier effect. d. U.S. consumers would spend all of their tax cut.