The unstable isotope 234Th decays by ? emission with a half-life of 24.5 days. The initial decay rate of the sample was 9.9 × 1013 Bq. (1 u = 1.6605 × 10-27 kg)
(a) What mass of 234Th was initially present?
(b) What is the decay rate after 68 days?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: (a) 0.12 g (b) 1.4 × 1013 Bq
You might also like to view...
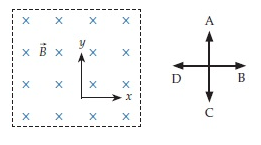 Consider a primed frame that moves in the +x direction with respect to the unprimed frame. Choose from the answers above and to the right to indicate the direction of the electric field in the primed frame.
Consider a primed frame that moves in the +x direction with respect to the unprimed frame. Choose from the answers above and to the right to indicate the direction of the electric field in the primed frame.
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. Toward the viewer F. Away from the viewer T. There is no field of this type.
Spectral lines from Galaxy B are redshifted from their rest wavelengths twice as much as the spectral lines from Galaxy B. According to Hubble's law, what can you say about their approximate relative distances?
A) Galaxy A is twice as far as Galaxy B. B) Galaxy B is four times as far as Galaxy A. C) Galaxy B is twice as far as Galaxy A. D) Galaxy A is four times as far as Galaxy B. E) Not enough information to say; you need to know Hubble's constant to answer this question.
Why does the surface of Triton appear so young?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following descriptions best describes the process by which energy is released in a conventional nuclear reactor?
A) The radiation given off by a naturally radioactive substance, uranium, is collected and used to make steam. B) Uranium is reacted with oxygen in a combustion process that releases large amounts of radioactivity and heat. C) Uranium, when bombarded by neutrons, splits into fragments and releases two or three neutrons, and these neutrons in turn strike more uranium nuclei that split, thereby setting off a chain reaction that releases energy. D) Deuterium and tritium are joined together to form helium. E) A uranium nucleus is energized to an excited state by neutron irradiation, and it then decays by emitting beta rays and gamma rays that heat water and create steam.