Assume that we want to drive our economy out of recession by generating a $400 billion change in real GDP. The MPC is 0.80. Which of the following policy prescriptions would generate the targeted $400 billion change in income?
A. $120 billion increase in government spending and $50 billion increase in tax revenue.
B. $140 billion increase in government spending and $70 billion increase in tax revenue.
C. $160 billion increase in government spending and $120 billion increase in tax revenue.
D. $220 billion increase in government spending and $100 billion increase in tax revenue.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Which one of the following people is not considered by the BLS as belonging to the labor force?
a. a full-time student at Nassau Community College who devotes all her time to her classes b. Roger Cherrier, who works 30 hours a week at Burger King and goes to school at night c. David Reinblatt, who was fired last week and immediately started searching for a new job d. the President of the United States e. Matt George, who plays professional hockey for the minor league team the Hershey Bears and concedes that he would play for nothing because of the love of the sport
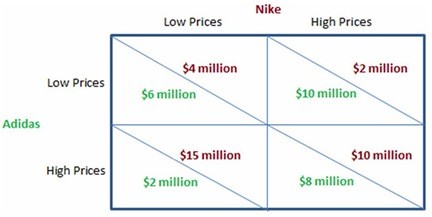 According to the figure shown, if Nike charges a high price, then Adidas should:
According to the figure shown, if Nike charges a high price, then Adidas should:
A. leave the market. B. give an ultimatum. C. charge a high price. D. charge a low price.
Under the gold standard system, if the par exchange rate is $1 = 2 pounds, but the market exchange rate in the United Kingdom is $1 = 1 pound, then a person interested in arbitrage would:
A) buy dollars in the United Kingdom to be shipped to the United States and exchanged for a larger quantity of gold. B) find that it is not possible to engage in arbitrage. C) convert dollars into pounds in the United States and sell it for gold in the United Kingdom. D) lose money by trying to exploit any price difference.
Henry has been thinking about purchasing a corporate bond but is afraid that the bond will lose value. He has decided to hold money instead. This is known as the
A. money balance demand for money. B. transactions demand for money. C. precautionary demand for money. D. asset demand for money.