Compound X enters a steady state compressor as a gas at P1=0.5 bar and T1=300 K, and leaves the compressor at P2=15 bar and T2=600 K. (These are the actual temperature and pressure of the exiting stream.) Then it enters a steady state heat exchanger in which it is cooled and condensed into a liquid at P3=15 bar and T3=200 K.
X has the following properties:
Critical temperature T=250 K
Critical pressure P=40 bar
Acentric factor ?=0.2
Ideal gas heat capacity CP* = 5R
At temperatures equal to or below 250 K, it can be modeled using the Peng-Robinson EOS
At pressures below 1 bar, it can be modeled as an ideal gas
At the conditions of the compressor outlet (2), it can be modeled using the following EOS:
PV = RT + (BP3)
Where B = -4 cm3mol-1bar-2
Prove that ((??H)/?P)_T= ?V- T((??V)/?T)_P
Find a general algebraic expression for the residual molar enthalpy HR, in terms of P, V , T and/or constants, that results from the equation of state PV = RT + (BP3).
Find the change in molar enthalpy for the gas as it goes through the compressor (H2-H1).
Determine the Peng-Robinson parameters a and b for this compound at a temperature of 200 K.
The three solutions of the Peng-Robinson for V at T=200 K and P=15 bar are V = 60.2, 326.3 and 681.6 cm3/mol. Determine the compressibility factor Z for the liquid leaving the heat exchanger.
Suppose you wanted to use the Lee-Kesler method, rather than the Peng-Robinson equation, to model the liquid leaving the heat exchanger (T3, P3). Use the figures in Chapter 7 to estimate the residual molar entropy S3R of this liquid.
Y is another compound in the same chemical family as X. Y has a critical temperature of 300 K and a critical pressure of 30 bar. At what temperature and pressure would you expect compound Y to have a compressibility factor (Z) identical to the one you calculated in part E?
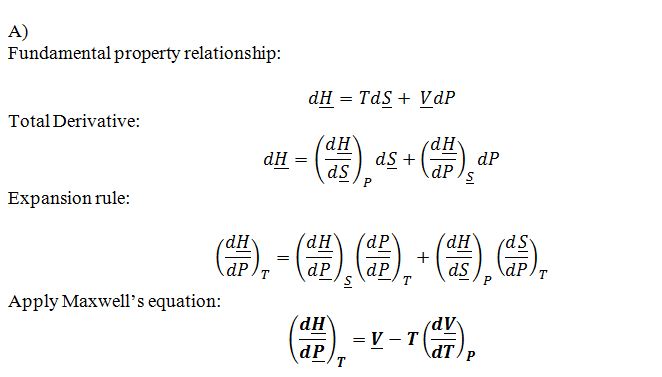
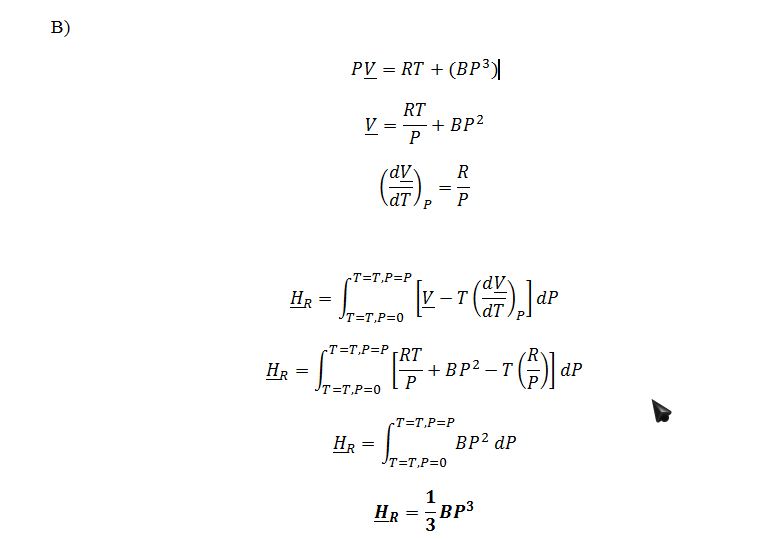


E) Of the three solutions to the Peng-Robinson equation given, 60.2 cm3/mol is the value for the liquid molar volume because it is the smallest of the three.
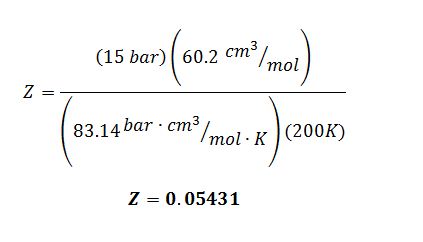

Using Figures 7-18 and 7-19:
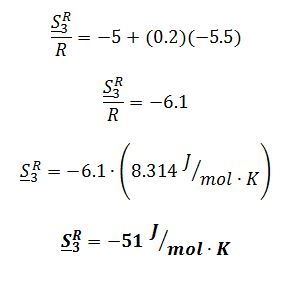
G) Apply principle of corresponding states:
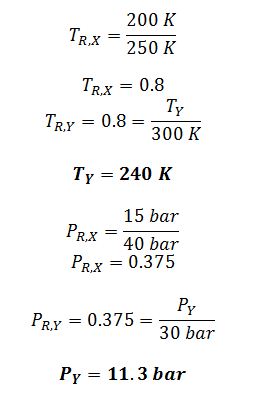
You might also like to view...
Use MATLAB to find the voltages at nodes a, b, c, and d in the circuit of Fig. 3.77.
 FIGURE 1.png)
In a direct expansion chiller, the chilled water is circulated:
A) Over the outside of the chiller shell. B) Through the compressor water cooling jacket. C) Through the inside of the chiller tubes. D) Over the outside of the chiller tubes.
Which software language is made up of binary or hexadecimal numbers?
A) machine code B) BASIC language C) C language D) assembly language
Letter F is pointing to a _____
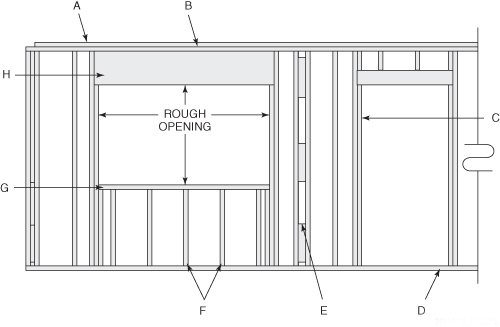
a. trimmer stud
b. king stud
c. cripple stud
d. common stud