International monetary analysis focuses on
A) the real side of the international economy.
B) the international trade side of the international economy.
C) the international investment side of the international economy.
D) the issues of international cooperation between Central Banks.
E) the monetary side of the international economy, such as currency exchange.
E
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. Moving from demand curve D1 to demand curve D2 could be caused by a(n): 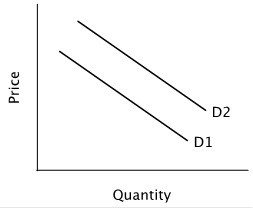
A. increase in the price of a complement. B. decrease in the product's expected future price. C. increase in the price of a close substitute. D. increase in quantity supplied.
Refer to Figure 22-4. Suppose the economy gains more capital per hour worked and experiences technological change. This is shown in the figure above by the movement from
A) E to B to D. B) A to E. C) A to B to C. D) A to D.
According to rational expectations theory,
A) increasing the money supply to reduce unemployment will always be successful. B) decreasing the money supply to reduce unemployment will usually be successful. C) increasing the money supply to reduce unemployment will not be successful because of an offsetting decrease in prices. D) increasing the money supply to reduce unemployment will not be successful because of an offsetting increase in prices.
By the height of the housing bubble in 2005 and early 2006, lenders had greatly loosened the standards for obtaining a mortgage loan, with many mortgages being granted to sub-prime borrowers ________ and "Alt-A" borrowers ________
A) with flawed credit histories; who did not document their incomes B) who borrowed money at rates below the prime interest rate; who had AAA credit ratings C) who borrowed more than 120 percent of the value of the house; with no proof of U.S. citizenship D) who purchased homes in depressed housing markets; who purchased homes which were repossessed by government agencies.