If a technological advance lowers a firm's production costs, why do prices typically fall? Shouldn't the firm maintain the same price and earn economic profit?
While any firm would like to maintain the higher price and experience economic profit, competition prevents this. Any technological advances (with the exception of discoveries covered by patents and trademarks) are likely to be available to all firms. As these technological advances lower costs, firms lower their prices to compete customers away from other sellers. This process occurs until the market price reflects the long-run equilibrium condition of zero economic profit.
You might also like to view...
The policy tool of "credit easing" refers to the
A) Fed's purchase of private securities to stimulate banks' lending. B) Fed's requirement that the federal government must lend to directly to home buyers. C) federal government's requirement that the Fed must lend directly to home buyers. D) Fed's lowering of the federal funds rate to zero. E) Treasury's issuance of federal debt to finance home buying.
In what ways do economists and policymakers who believe that market-based reforms are the key to improving the health care system criticize the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA)?
What will be an ideal response?
There are only two goods for John to consume: food and clothing. If clothing is an inferior good for John when his income rises to $100,000, then food is
A) also an inferior good. B) a normal good. C) Either inferior or normal could be possible. D) Not enough information
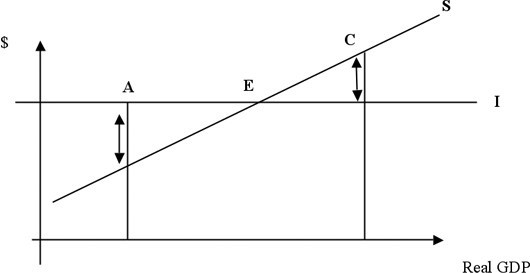 In the above figure, point E represents the level of real GDP at which planned saving equals planned investment. At point C
In the above figure, point E represents the level of real GDP at which planned saving equals planned investment. At point C
A. unplanned inventories increase. B. changes in inventories cannot be determined. C. unplanned inventories decrease. D. unused industrial capacity exists in the economy.