In the ___________ model of decision making, each decision builds on the previous one, forming a sequence of decisions, such as the steps involved in preparing a meal
a. Central-satellite
b. Foa & Foa
c. Elbing
d. Chain
D
You might also like to view...
What is an indifference curve?
A) It is a curve that shows the combinations of consumption bundles that give the consumer the same utility. B) It is a curve that shows the total utility and the marginal utility derived from consuming a bundle of goods. C) It is a curve that ranks a consumer's preference for various consumption bundles. D) It is a curve that shows the tradeoff a consumer faces among different combinations of consumption bundles.
When price is greater than both marginal cost and average variable cost, the perfectly competitive firm
A) is maximizing economic profit. B) should increase its level of output. C) should reduce its level of output. D) should stop production.
To an economist, scarcity means that:
a. it is very time-consuming to find a good. b. at a zero price, the available quantity of a good is insufficient to meet people's wants. c. a good is unavailable even at very high prices. d. at the current market price, the amount available is less than the amount that people want and are willing to pay for. e. resources are unlimited but people's desires are limited.
Refer to the following figure showing demand and marginal revenue for a monopoly.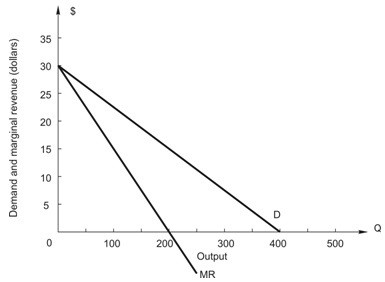 At any price above $________ demand is elastic.
At any price above $________ demand is elastic.
A. $5 B. $15 C. zero D. $20 E. $10