Look up everything you can find about iron seeding of the oceans and see if you can decide what you think we should do
What will be an ideal response?
Students would have to come up with their own conclusions, but here are some arguments for both sides.
Pro Side
- It does promote large amounts of phytoplankton growth when tested.
- Huge cores of phytoplankton have been found in ice from various ice ages.
- In the deeper parts of the ocean the carbon would be sequestered for thousands of years.
- Approximately one-half of the photosynthesis takes place in the oceans but oceans make up three-fourths of Earth's surface. Seeding would help equalize this disparity.
- The Earth's warming is reducing the productivity of the oceans. Iron seeding could help reverse this trend.
- The process is simple: dump a tanker of iron into an open part of the ocean.
Con Side
- It promotes large amounts of zooplankton growth.
- Some are also worried that the increased mass of plankton will release additional methane and nitrous oxide, which might increase greenhouse gases, and have a counterproductive effect.
- May give people the feeling they have a "license to pollute" because carbon is being sequestered elsewhere (i.e. people drive more or use more electricity).
- Iron disperses in the ocean rapidly so it would be a very short-term gain and would take huge amounts of iron to sustain bloom activity.
- There is little regulation of the ocean so there is a high probability of something going wrong.
- It is 10 to 100 times less efficient than other natural means of carbon sequestering.
- Iron seeding could trigger an ice age (started by a quip by John Martin, the first to suggest iron seeding in 1993). (Earth Magazine, 1996)
- The amount of iron needed is too expensive in comparison to the benefits.
- May interfere with natural food webs in the area.
- Currents and upwelling from the deep vary from one area of the ocean to another and both must be considered when planning the seeding.
You might also like to view...
Distinguish between atoms and molecules. Which is made of which?
What will be an ideal response?
What is an example of authigenic sediment?
a. Quartz sand b. Phosphorite deposits c. Volcanic dust d. Diatomaceous ooze e. Tektite spheres
On this map, identify the letter that is over an island arc.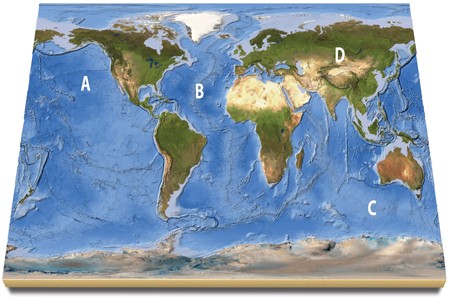
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. feature is not labeled
Which of the following is not a principle of Ecosystem function?
A) Ecosystems are always open to gains and losses of matter and energy. B) Ecosystem change is inevitable and essential. C) Matter and energy are neither created nor destroyed. D) Ecosystem's processes are self-regulated by interactions among their living and nonliving components. E) Ecosystems have distinct boundaries that are influenced by the abiotic factors in the ecosystem.