Nutrients undergo the last stages of digestion by enzymes located on the cells of the small intestine; then the nutrients are absorbed by these same cells by way of various membrane transport processes. Adipose cells absorb and store excess food energy in the form of fat. You and the other students in the physiology lab you are taking are doing an analysis of cell membrane composition, on unknown
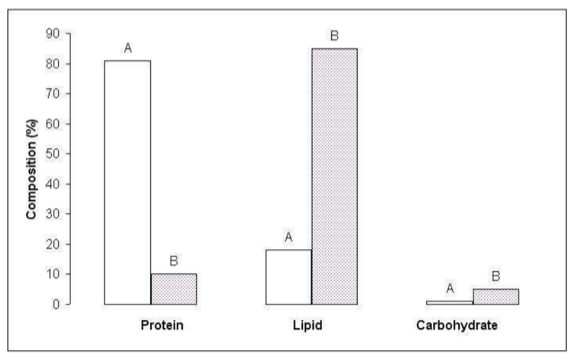
animal tissue samples labeled A and B. All lab groups determined that sample A contained, on average, 81% protein, 18% lipid, and 1% carbohydrate. Sample B contained 85% lipid, 10% protein, and 5% carbohydrate. Sketch a graph of the class data. You now have to make a logical conclusion as to which sample is more likely to be intestine and which is adipose tissue. What do you conclude, and why?
What will be an ideal response?
A bar graph would be appropriate, as in the figure below. The presence of digestive enzymes and membrane transporters in small intestine cells indicate there should be a significant amount of protein present. Adipose cells, on the other hand, are relatively inactive and can passively absorb lipids by way of simple diffusion through the membrane phospholipids. Adipose tissue is expected, therefore, to consist primarily of lipids. Sample A is most likely small intestine, and sample B adipose.
You might also like to view...
Which of the types of receptors listed below is primarily used for detecting light rays under bright light conditions?
a) olfactory hair cells b) rods c) cones d) ganglion neurons e) amacrine cells
What is the half-life of a signal?
What will be an ideal response?
An electroencephalogram
a. is primarily a record of action potential activity in the cerebral cortex b. represents the momentary collective postsynaptic activity in the cerebral cortex c. displays larger brain waves when the eyes are open than when the eyes are closed d. displays impulse activity deep inside the brain e. is useful in all of the ways mentioned above
A network or braid; a network of nerves.
A. Ganglia B. Fibers C. Plexus D. Ligaments