Water is most dense and thus heaviest at 4°C. At 0°C, ice forms and can float on liquid water. Suppose ice were most dense at 0°C. What would happen in a lake at this temperature?
A. The ice would cover the surface of the aquatic system and would never melt.
B. The ice would cover the bottom of the aquatic system and would build up in layers over time.
C. The cold temperatures and the subsequent ice formation would prevent hydrogen bonds from forming between the water molecules, thus causing the existing ice crystals to become disassociated from each other.
D. Ice would not form because solids are always less dense than liquids.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The lens is bathed on both sides by
a. the vitreous humor. b. the aqueous humor. c. blood. d. a solution rich in glucose. e. the enzymes for proper function.
All microbicidal agents are sterilants.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Refer to Figure 13-3. The component labeled B is:
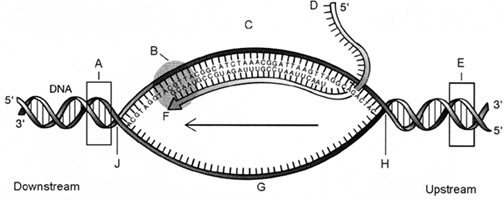
a. DNase.
b. DNA polymerase.
c. RNA primase.
d. RNA polymerase.
e. reverse transcriptase
You are a physician treating a patient with cancer. Traditional chemotherapy has not been working on this patient, so you prescribe a new class of drugs called taxanes, which inhibit microtubule function. Your patient asks you how they work. How would
you explain to your patient how these drugs work? What will be an ideal response?