Refer to the information provided in Table 14.3 below to answer the question that follows.
Table 14.3B's Strategy
?AdvertiseDon't Advertise??A's profit $75 millionA's profit $200 million?AdvertiseB's profit $75 millionB's profit $50 millionA's Strategy????Don'tA's profit $50 millionA's profit $100 million?AdvertiseB's profit $200 millionB's profit $100 millionRefer to Table 14.3. The result of this game is a prisoners' dilemma. In which of the following cases is it most likely that the firms will be able to overcome the prisoners' dilemma?
A. government intervention
B. when both firms follow a maximin strategy
C. repeated play
D. a single interaction
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
A perfectly competitive producer is
A. a "price maker." B. a "price taker." C. both a "price maker" and a "price taker." D. neither a "price maker" nor a "price taker."
Microeconomics can be used by governments to predict the impacts of a policy and suggest solutions to problems
What will be an ideal response?
In general, as units of resource inputs rise, the marginal revenue product
A. rises faster under imperfect competition than under perfect competition. B. rises faster under perfect competition than under imperfect competition. C. falls faster under perfect competition than under imperfect competition. D. falls faster under imperfect competition than under perfect competition.
If the world supply curve is SW0,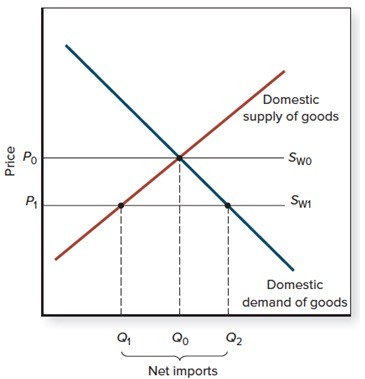
A. domestic quantity supplied is unrelated to domestic quantity demanded. B. domestic quantity supplied exceeds domestic quantity demanded. C. domestic quantity supplied equals domestic quantity demanded. D. domestic quantity supplied is less than domestic quantity demanded.