Met" refers to a gene that governs a cell's ability to synthesize methionine from inorganic precursors. What does the designation "met-" indicate?
a. that the allele is normal (i.e., wild type)
b. that the bacterium is biologically active
c. that the bacterium is biologically inactive
d. that the allele is the mutant allele
Answer: d. that the allele is the mutant allele
You might also like to view...
During the initiation of nitrogen-fixation nodules, a host plant with genetic mutations releases altered forms of flavonoids. What is the likely consequence of this?
A. Infection threads will grow in the wrong direction. B. More nodules will form than necessary. C. The bacteria will not produce any Nod factors. D. Nodules will be misshapen. E. The bacterial will produce higher levels of Nod factors.
The letter “E” in the above figure represents
a. sclerenchyma fibers. b. parenchyma. c. xylem. d. epidermis. e. phloem.
If bacteria are infected with a bacteriophage and briefly exposed to radioactive uracil, what results would you expect to see immediately after exposure?
A) radioactive mRNA in the cytoplasm B) radioactive mRNA in the nucleus C) radioactive DNA in the cytoplasm D) radioactive DNA in the nucleus E) radioactive proteins in the nuclear membrane
The structures labeled 2 in Figure 43-2 are the:
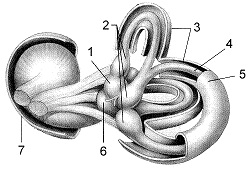
a. ampullae.
b. cochleae.
c. utricles.
d. semicircular canals.
e. bony labyrinth