The change in nominal GDP will always exceed the change in real GDP when nominal GDP is
a. increasing and prices are unchanged.
b. increasing and prices are decreasing.
c. decreasing and prices are decreasing.
d. increasing and prices are increasing.
D
You might also like to view...
How will an increase in physical capital affect labor productivity, labor demand, and potential GDP?
What will be an ideal response?
Speculative demand for money is a(n):
a. positive function of prices. b. inverse function of prices. c. positive function of interest rates. d. inverse function of interest rates. e. function of unexpected needs.
Other things the same, if the U.S. interest rate falls, then U.S. residents will want to purchase
a. more foreign assets, which increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded. b. fewer foreign assets, which decreases the quantity of loanable funds demanded. c. more foreign assets, which increase the quantity of loanable funds supplied. d. fewer foreign assets, which decreases the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
Theoretically, profit maximization occurs at P* and q* in the short run. However, empirical work suggests that oligopolists often actually charge P1. What would be the motivation for this action?
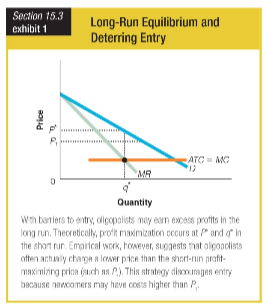
a. to increase P 1 above the profit maximization price over the short run
b. to reduce the entry initiative for new firms attracted by long-run economic profit
c. to increase the profit maximization price over the short run
d. to reduce the entry initiative for new firms attracted by zero long-run economic profit