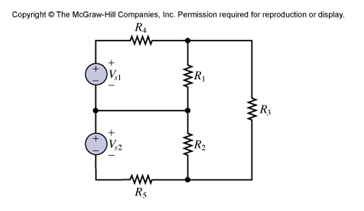
For the circuit of Figure P3.22 determine: a. The most efficient way to solve for the voltage\ across R3. Prove your case. b. The voltage across R3.
VS1 = VS2 = 110 V
R1 = 500 m? R2 = 167 m?
R3 = 700 m?
R4 = 200 m? R5 = 333 m?
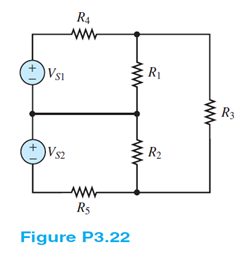
Known quantities:
Circuit shown in Figure P3.22
Find:
a. The most efficient way to solve for the voltage across R3. Prove your case.
b. The voltage across R3.
Analysis:
a) There are 3 meshes and 3 mesh currents requiring the solution of 3 simultaneous equations. Only one of these mesh currents is required to determine, using Ohm's Law, the voltage across R3.
If the terminal (or node) between the two voltage sources is made the ground (or reference) node, then three node voltages are known (the ground or reference voltage and the two source voltages). This leaves only two unknown node voltages (the voltages across R1, VR1, and across R2, VR2). Both these voltages are required to determine, using KVL, the voltage across R3, VR3.
A difficult choice. Choose node analysis due to the smaller number of unknowns. Specify the nodes. Choose one node as the ground node. In KCL, assume unknown currents flow out.
b)
You might also like to view...
The manner in which amino acids are linked chemically into peptide chains probably
accounts for some of wool's unique properties. A. True B. False
All of the following are types of optical storage except ________
A) QIC B) CD-RW C) WORM D) DVD
ASTM and SAE created a combined numbering system for metals and alloys.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
An example of a compound is ____.
A. carbon dioxide B. tungsten C. salt D. salt water