In this problem the Peng-Robinson equation is used to model n-octane at 5 bar and 500 K. For n-octane, Tc=568.70 K, Pc=24.90 bar and ?=0.399. The three solutions for the molar volume of n-octane at this temperature and pressure are:
V = 249.58 cm3/mol, 648 cm3/mol, and 7270 cm3/mol
A) Calculate the values of the Peng-Robinson parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ for octane at T=500 K.
B) Calculate the fugacity of n-octane in the liquid and vapor phases at 500 K and 5 bar, according to the Peng-Robinson equation. If you have no answer to part A, use a=4.5x107 bar cm6 mol-2 and b = 150 cm3/mol
C) Based on your answer to part B, is the vapor pressure of octane at 500 K greater than, or less than, 5 bar?

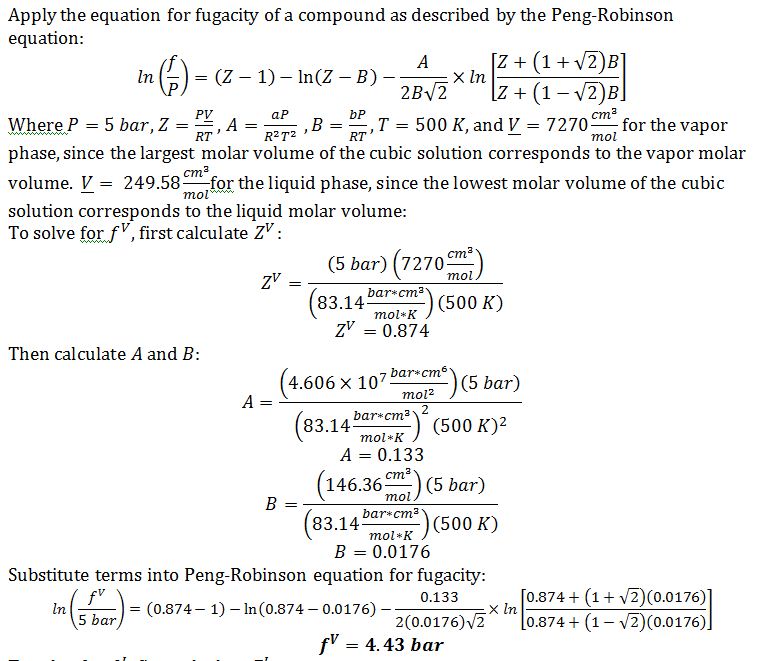
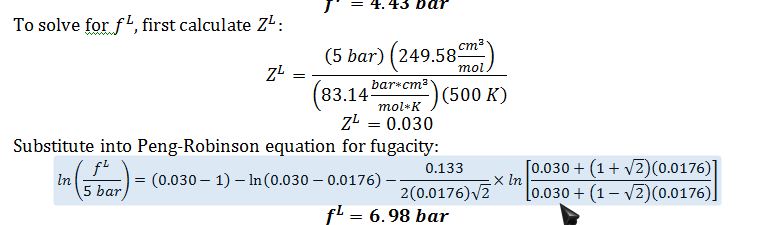
Since f^V
ln(f/P)=??G-?G?^ig/RT
Therefore, the vapor pressure must be higher than 5 bar (the pressure at which the fugacity values were calculated).
You might also like to view...
The sentiment of fear and opposition to open immigration was called
A. the cult of domesticity. B. nativism. C. racism. D. rugged individualism. E. patriotism.
The primary source of heat for a year-round packaged air conditioner is _____.
a. electricity b. natural gas c. hot water d. steam
In the op amp circuit in Fig. 11.42, find the total average power absorbed by the resistors.
 FIGURE 1.png)
Assist hybrids use an engine as the primary source of power for propulsion.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)